Multiple Zeta Values
by Akhilesh P.
Computing Multiple Zeta values (Euler-Zagier numbers)
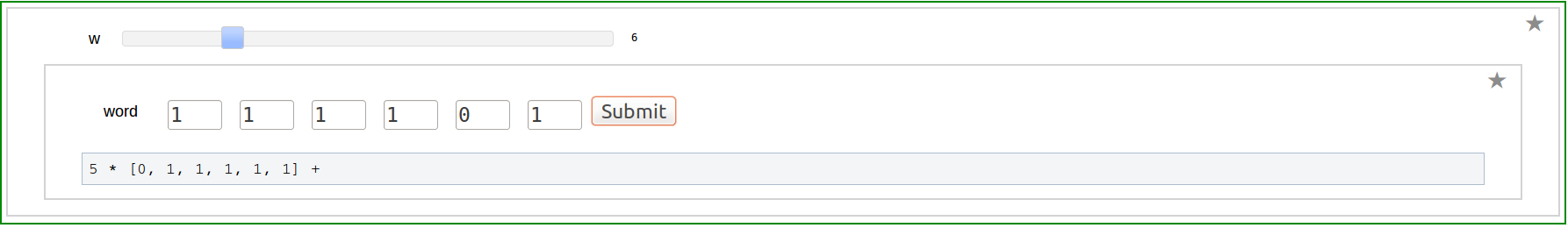
Word Input

Composition Input
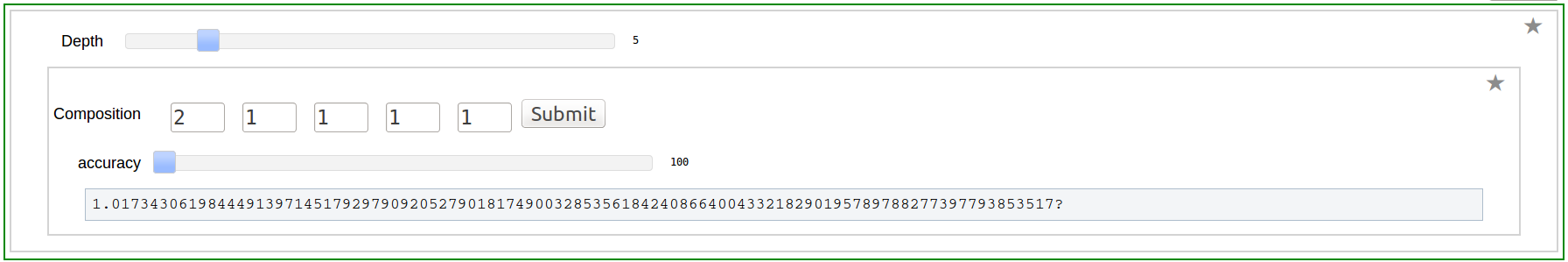
Program to Compute Integer Relation between Multiple Zeta Values (Euler-Zagier numbers)
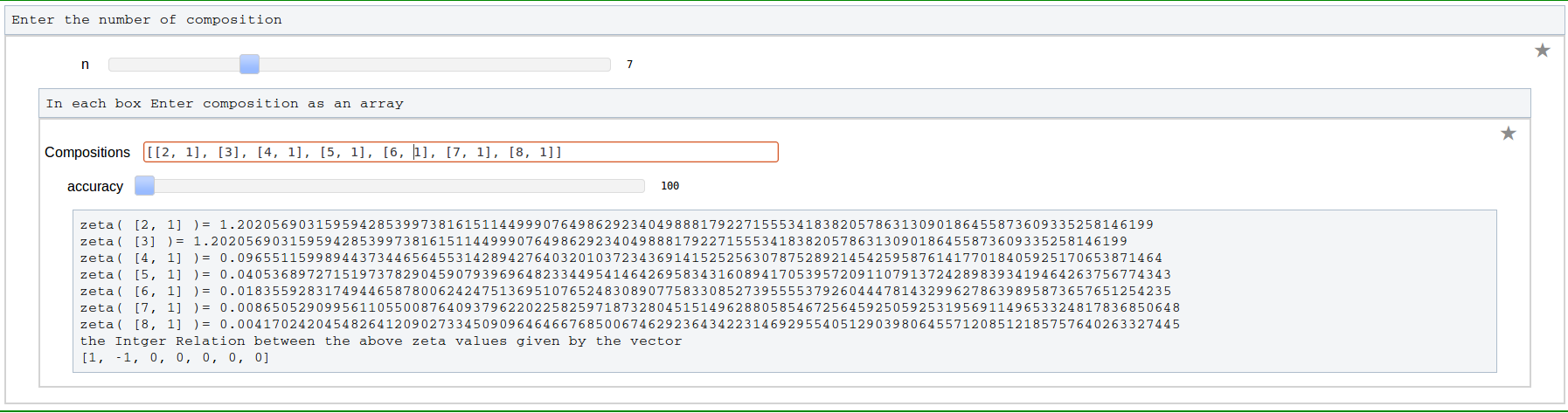
Word to composition
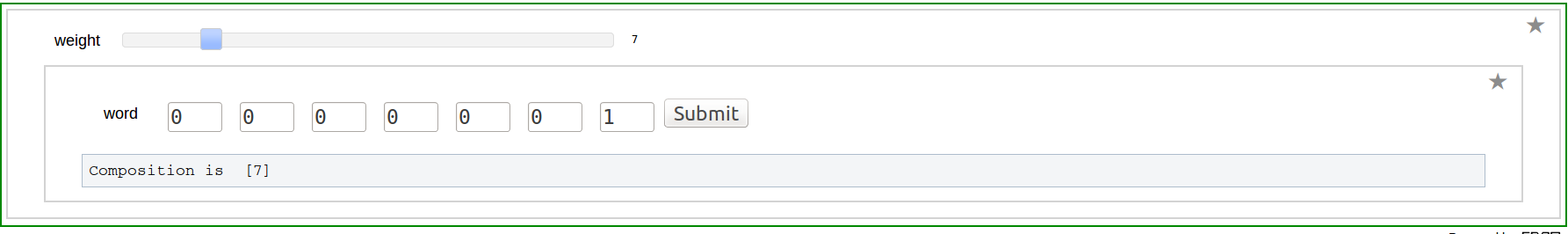
Composition to Word
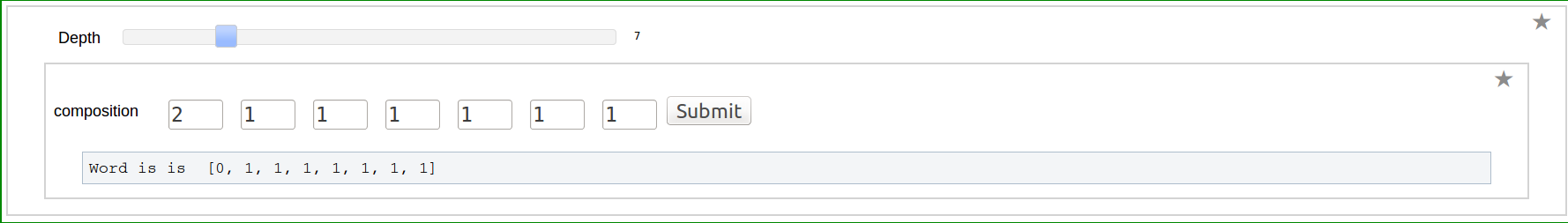
Dual of a Word
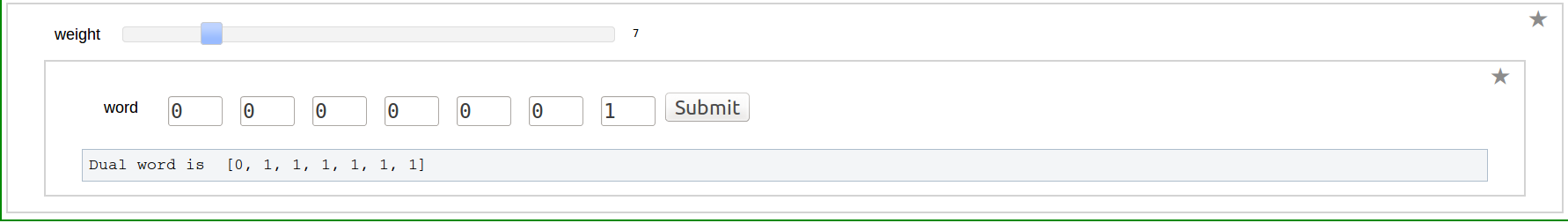
Shuffle product of two Words
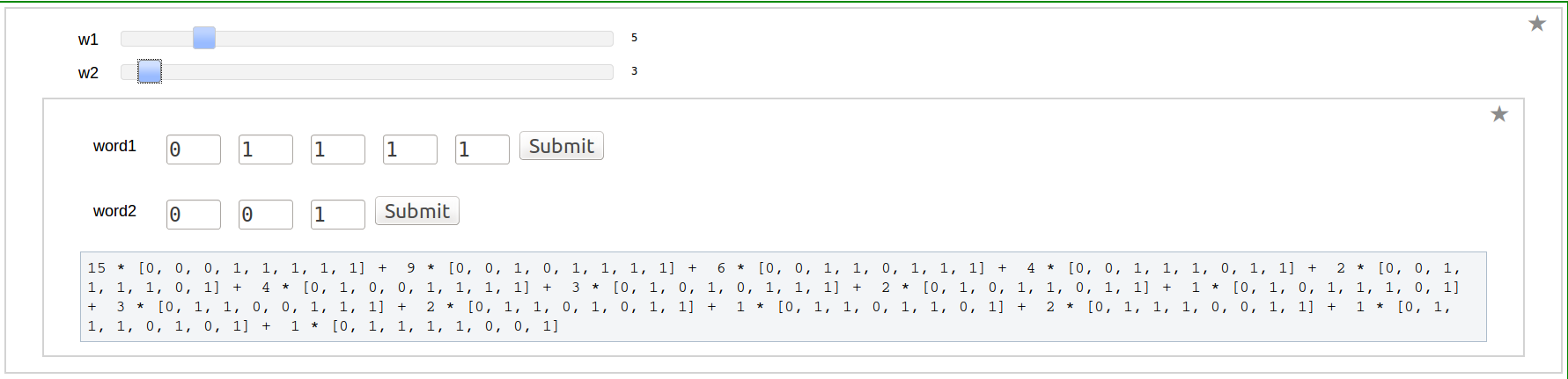
Shuffle Regularization at 0
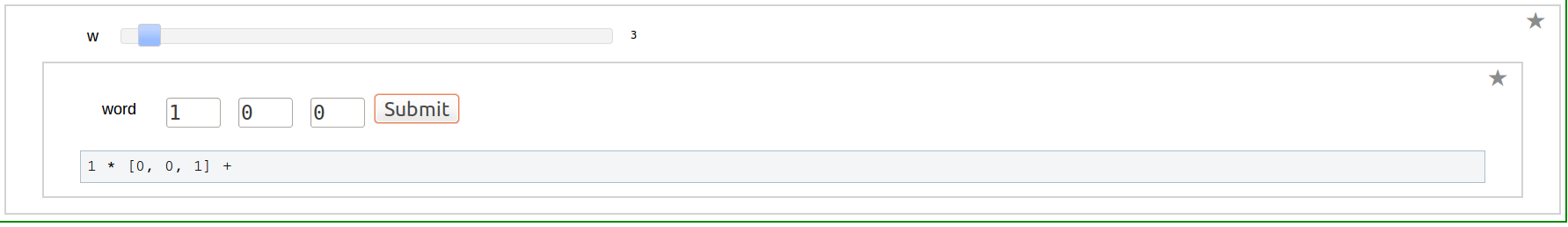
Shuffle Regularization at 1