|
Size: 7713
Comment:
|
Size: 9830
Comment: Fixed Cellular Automaton to work correctly for rules where background is ones (such as 255) and made matrix display in opposite colours, as is conventional.
|
| Deletions are marked like this. | Additions are marked like this. |
| Line 8: | Line 8: |
| by Marshall Hampton | by Marshall Hampton. When the two frequencies are well seperated, we hear the right hand side of the identity. When they start getting close, we hear the higher-pitched factor in the left-hand side modulated by the lower-pitched envelope. |
| Line 35: | Line 35: |
| s2str = '' for x in s2f: s2str += wave.struct.pack('h',x) lab=str(float(freq_ratio)) |
s2str = ''.join(wave.struct.pack('h',x) for x in s2f) lab="%1.2f"%float(freq_ratio) |
| Line 48: | Line 46: |
| == Karplus-Strong algorithm for plucked and percussive sound generation == by Marshall Hampton {{{ import wave class SoundFile: def __init__(self, signal,lab=''): self.file = wave.open('./test' + lab + '.wav', 'wb') self.signal = signal self.sr = 44100 def write(self): self.file.setparams((1, 2, self.sr, 44100*4, 'NONE', 'noncompressed')) self.file.writeframes(self.signal) self.file.close() mypi = float(pi) from math import sin def ks(delay,length,blend = 0,filler=None,stretch=0): if filler == None: filler = [randint(-16383,16383) for q in range(delay+1)] outsig = filler[:] index = len(filler) while len(outsig) < length: s = random() if s > stretch: b = random() if b < 1-blend: newvalue = (outsig[index-delay]+outsig[index-delay-1])*.5 else: newvalue = -(outsig[index-delay]+outsig[index-delay-1])*.5 else: newvalue = outsig[index-delay] outsig.append(newvalue) index += 1 return [int(round(x)) for x in outsig] @interact def sinsound(delay = slider([int(2^i) for i in range(2,10)], default=100, label="initial delay"), blend=slider(srange(0,1,.01,include_endpoint=True),default=0,label="blend factor"), stretch=slider(srange(0,1,.01,include_endpoint=True),default=0,label="stretch factor")): s2f = ks(delay,int(44100*(1/2)),blend=blend,stretch=stretch) for i in range(12): s2f = s2f + ks(int(2^((12+i)/12.0)*delay),int(44100*(1/2)),blend=blend, stretch=stretch) html("Karplus-Strong algorithm with blending and delay stretching") html("<br>K. Karplus and A. Strong, <em>Digital synthesis of plucked string and drum timbres</em>, \nComputer Music Journal 7 (2) (1983), 43–55.<br>") html("Initial waveform:") show(list_plot(s2f[0:2000],plotjoined=True), figsize = [7,3.5]) html("Waveform after stabilization:") show(list_plot(s2f[20000:22000],plotjoined=True), figsize = [7,3.5]) s2str = ''.join(wave.struct.pack('h',x) for x in s2f) lab="" f = SoundFile(s2str,lab=lab) f.write() html('<embed src="https:./test'+ lab +'.wav" width="200" height="100"></embed>') }}} {{attachment:KarplusStrong.png}} |
|
| Line 62: | Line 118: |
| XY = X.intersection(Y) XZ = X.intersection(Z) YZ = Y.intersection(Z) XYZ = XY.intersection(Z) |
XY = X & Y XZ = X & Z YZ = Y & Z XYZ = XY & Z |
| Line 92: | Line 148: |
| Z = set(S[i]).intersection(S[(i+1)%3]).difference(set(XYZ)) | Z = (set(S[i]) & S[(i+1)%3]) - set(XYZ) |
| Line 149: | Line 205: |
| == A Random Walk == by William Stein {{{ html('<h1>A Random Walk</h1>') vv = []; nn = 0 @interact def foo(pts = checkbox(True, "Show points"), refresh = checkbox(False, "New random walk every time"), steps = (50,(10..500))): # We cache the walk in the global variable vv, so that # checking or unchecking the points checkbox doesn't change # the random walk. html("<h2>%s steps</h2>"%steps) global vv if refresh or len(vv) == 0: s = 0; v = [(0,0)] for i in range(steps): s += random() - 0.5 v.append((i, s)) vv = v elif len(vv) != steps: # Add or subtract some points s = vv[-1][1]; j = len(vv) for i in range(steps - len(vv)): s += random() - 0.5 vv.append((i+j,s)) v = vv[:steps] else: v = vv L = line(v, rgbcolor='#4a8de2') if pts: L += points(v, pointsize=10, rgbcolor='red') show(L, xmin=0, figsize=[8,3]) }}} {{attachment:randomwalk.png}} == 3D Random Walk == {{{ @interact def rwalk3d(n=(50,1000), frame=True): pnt = [0,0,0] v = [copy(pnt)] for i in range(n): pnt[0] += random()-0.5 pnt[1] += random()-0.5 pnt[2] += random()-0.5 v.append(copy(pnt)) show(line3d(v,color='black'),aspect_ratio=[1,1,1],frame=frame) }}} {{attachment:randomwalk3d.png}} |
|
| Line 228: | Line 233: |
| edge_lines = edge_lines + line([verts[an_edge[0]], verts[an_edge[1][0]]]) edge_lines = edge_lines + line([verts[an_edge[0]], verts[an_edge[1][1]]]) |
edge_lines += line([verts[an_edge[0]], verts[an_edge[1][0]]]) edge_lines += line([verts[an_edge[0]], verts[an_edge[1][1]]]) |
| Line 235: | Line 240: |
| triangle_sum = triangle_sum + polygon(temp_list, alpha = .5, rgbcolor = (1,0,0)) | triangle_sum += polygon(temp_list, alpha = .5, rgbcolor = (1,0,0)) |
| Line 241: | Line 246: |
| kite_sum = kite_sum + polygon(temp_list, alpha = .3,rgbcolor = (0,0,1)) | kite_sum += polygon(temp_list, alpha = .3,rgbcolor = (0,0,1)) |
| Line 243: | Line 248: |
| labels = labels + text('=', (-.2,.5), rgbcolor = (0,0,0)) | labels += text('=', (-.2,.5), rgbcolor = (0,0,0)) |
| Line 247: | Line 252: |
== Cellular Automata == by Pablo Angulo, Eviatar Bach {{{ from numpy import zeros def cellular(rule, N): '''Yields a matrix showing the evolution of a Wolfram's cellular automaton rule: determines how a cell's value is updated, depending on its neighbors N: number of iterations ''' M=zeros( (N,2*N+1), dtype=int) M[0,N]=1 for j in range(1,N): for k in range(0,2*N): l = 4*M[j-1,k-1] + 2*M[j-1,k] + M[j-1,k+1] M[j,k]=rule[ l ] return M[:,:-1] }}} {{{ def num2rule(number): if not 0 <= number <= 255: raise Exception('Invalid rule number') binary_digits = number.digits(base=2) return binary_digits + [0]*(8-len(binary_digits)) @interact def _( N=input_box(label='Number of iterations',default=100), rule_number=input_box(label='Rule number',default=110), size = slider(1, 11, step_size=1, default=6 ) ): rule = num2rule(rule_number) M = cellular(rule, N) plot_M = matrix_plot(M, cmap='binary') plot_M.show( figsize=[size,size]) }}} {{attachment:cellular.png}} |
Sage Interactions - Miscellaneous
goto interact main page
Contents
Hearing a trigonometric identity
by Marshall Hampton. When the two frequencies are well seperated, we hear the right hand side of the identity. When they start getting close, we hear the higher-pitched factor in the left-hand side modulated by the lower-pitched envelope.
import wave
class SoundFile:
def __init__(self, signal,lab=''):
self.file = wave.open('./test' + lab + '.wav', 'wb')
self.signal = signal
self.sr = 44100
def write(self):
self.file.setparams((1, 2, self.sr, 44100*4, 'NONE', 'noncompressed'))
self.file.writeframes(self.signal)
self.file.close()
mypi = float(pi)
from math import sin
@interact
def sinsound(freq_ratio = slider(0,1,1/144,1/12)):
hz1 = 440.0
hz2 = float(440.0*2^freq_ratio)
html('$\cos(\omega t) - \cos(\omega_0 t) = 2 \sin(\\frac{\omega + \omega_0}{2}t) \sin(\\frac{\omega - \omega_0}{2}t)$')
s2 = [sin(hz1*x*mypi*2)+sin(hz2*x*mypi*2) for x in srange(0,4,1/44100.0)]
s2m = max(s2)
s2f = [16384*x/s2m for x in s2]
s2str = ''.join(wave.struct.pack('h',x) for x in s2f)
lab="%1.2f"%float(freq_ratio)
f = SoundFile(s2str,lab=lab)
f.write()
pnum = 1500+int(500/freq_ratio)
show(list_plot(s2[0:pnum],plotjoined=True))
html('<embed src="https:./test'+ lab +'.wav" width="200" height="100"></embed>')
html('Frequencies: '+ '$\omega_0 = ' + str(hz1) + ' $, $\omega = '+latex(hz2) + '$')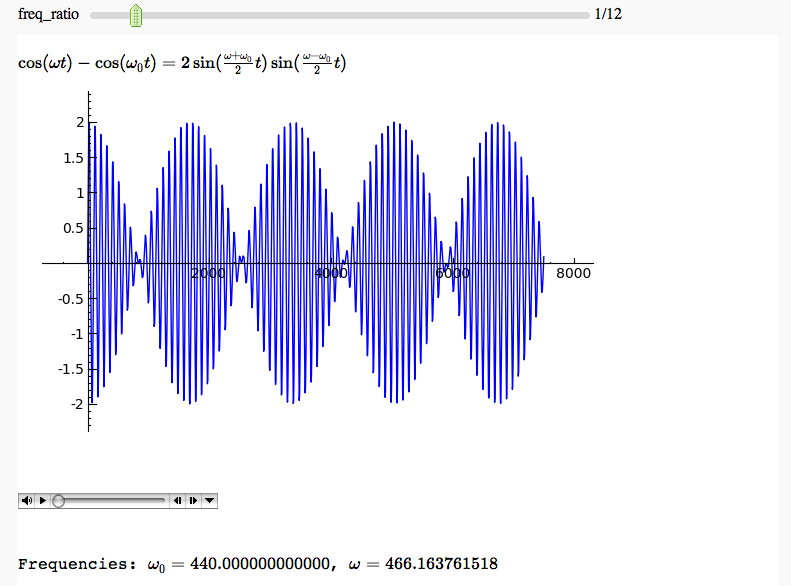
Karplus-Strong algorithm for plucked and percussive sound generation
by Marshall Hampton
import wave
class SoundFile:
def __init__(self, signal,lab=''):
self.file = wave.open('./test' + lab + '.wav', 'wb')
self.signal = signal
self.sr = 44100
def write(self):
self.file.setparams((1, 2, self.sr, 44100*4, 'NONE', 'noncompressed'))
self.file.writeframes(self.signal)
self.file.close()
mypi = float(pi)
from math import sin
def ks(delay,length,blend = 0,filler=None,stretch=0):
if filler == None:
filler = [randint(-16383,16383) for q in range(delay+1)]
outsig = filler[:]
index = len(filler)
while len(outsig) < length:
s = random()
if s > stretch:
b = random()
if b < 1-blend:
newvalue = (outsig[index-delay]+outsig[index-delay-1])*.5
else:
newvalue = -(outsig[index-delay]+outsig[index-delay-1])*.5
else:
newvalue = outsig[index-delay]
outsig.append(newvalue)
index += 1
return [int(round(x)) for x in outsig]
@interact
def sinsound(delay = slider([int(2^i) for i in range(2,10)], default=100, label="initial delay"), blend=slider(srange(0,1,.01,include_endpoint=True),default=0,label="blend factor"), stretch=slider(srange(0,1,.01,include_endpoint=True),default=0,label="stretch factor")):
s2f = ks(delay,int(44100*(1/2)),blend=blend,stretch=stretch)
for i in range(12):
s2f = s2f + ks(int(2^((12+i)/12.0)*delay),int(44100*(1/2)),blend=blend, stretch=stretch)
html("Karplus-Strong algorithm with blending and delay stretching")
html("<br>K. Karplus and A. Strong, <em>Digital synthesis of plucked string and drum timbres</em>, \nComputer Music Journal 7 (2) (1983), 43–55.<br>")
html("Initial waveform:")
show(list_plot(s2f[0:2000],plotjoined=True), figsize = [7,3.5])
html("Waveform after stabilization:")
show(list_plot(s2f[20000:22000],plotjoined=True), figsize = [7,3.5])
s2str = ''.join(wave.struct.pack('h',x) for x in s2f)
lab=""
f = SoundFile(s2str,lab=lab)
f.write()
html('<embed src="https:./test'+ lab +'.wav" width="200" height="100"></embed>')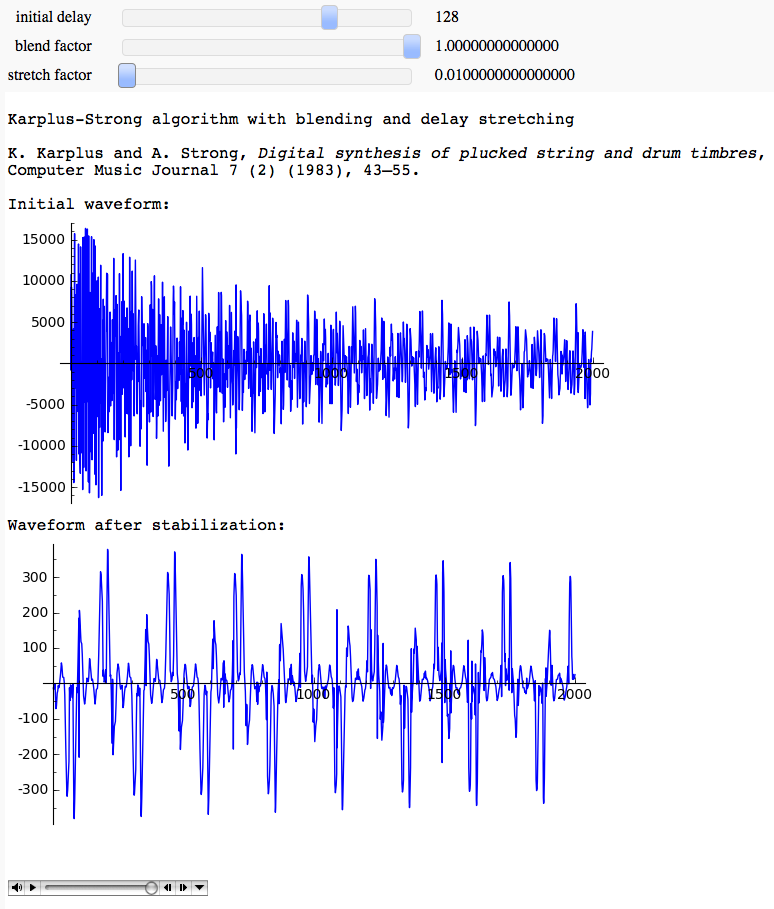
An Interactive Venn Diagram
def f(s, braces=True):
t = ', '.join(sorted(list(s)))
if braces: return '{' + t + '}'
return t
def g(s): return set(str(s).replace(',',' ').split())
@interact
def _(X='1,2,3,a', Y='2,a,3,4,apple', Z='a,b,10,apple'):
S = [g(X), g(Y), g(Z)]
X,Y,Z = S
XY = X & Y
XZ = X & Z
YZ = Y & Z
XYZ = XY & Z
html('<center>')
html("$X \cap Y$ = %s"%f(XY))
html("$X \cap Z$ = %s"%f(XZ))
html("$Y \cap Z$ = %s"%f(YZ))
html("$X \cap Y \cap Z$ = %s"%f(XYZ))
html('</center>')
centers = [(cos(n*2*pi/3), sin(n*2*pi/3)) for n in [0,1,2]]
scale = 1.7
clr = ['yellow', 'blue', 'green']
G = Graphics()
for i in range(len(S)):
G += circle(centers[i], scale, rgbcolor=clr[i],
fill=True, alpha=0.3)
for i in range(len(S)):
G += circle(centers[i], scale, rgbcolor='black')
# Plot what is in one but neither other
for i in range(len(S)):
Z = set(S[i])
for j in range(1,len(S)):
Z = Z.difference(S[(i+j)%3])
G += text(f(Z,braces=False), (1.5*centers[i][0],1.7*centers[i][1]), rgbcolor='black')
# Plot pairs of intersections
for i in range(len(S)):
Z = (set(S[i]) & S[(i+1)%3]) - set(XYZ)
C = (1.3*cos(i*2*pi/3 + pi/3), 1.3*sin(i*2*pi/3 + pi/3))
G += text(f(Z,braces=False), C, rgbcolor='black')
# Plot intersection of all three
G += text(f(XYZ,braces=False), (0,0), rgbcolor='black')
# Show it
G.show(aspect_ratio=1, axes=False)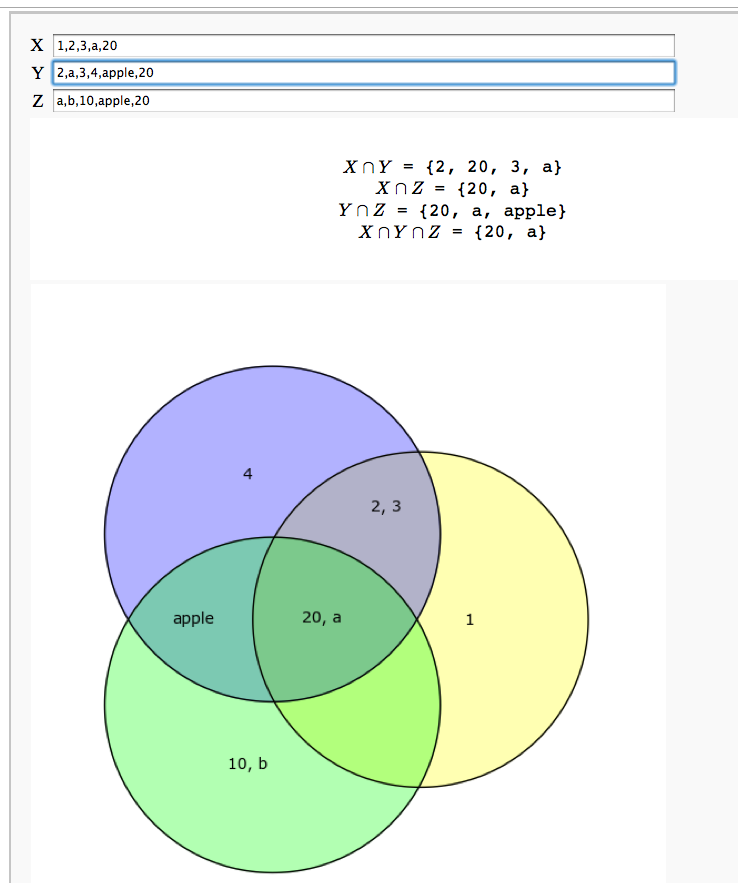
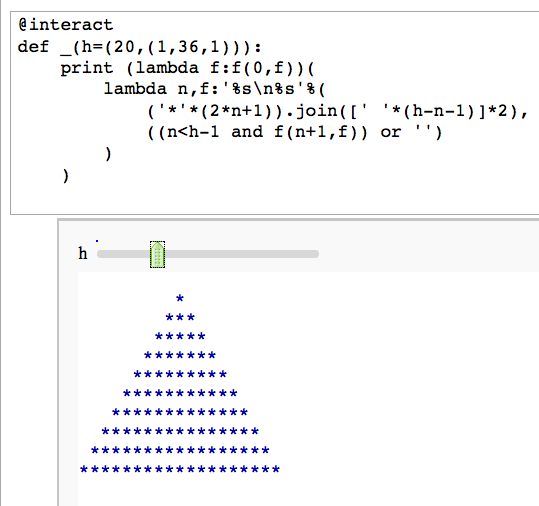
Unreadable code
by Igor Tolkov
@interact
def _(h=(20,(1,36,1))):
print (lambda f:f(0,f))(
lambda n,f:'%s\n%s'%(
('*'*(2*n+1)).join([' '*(h-n-1)]*2),
((n<h-1 and f(n+1,f)) or '')
)
)
Profile a snippet of code
html('<h2>Profile the given input</h2>')
import cProfile; import profile
@interact
def _(cmd = ("Statement", '2 + 2'),
do_preparse=("Preparse?", True), cprof =("cProfile?", False)):
if do_preparse: cmd = preparse(cmd)
print "<html>" # trick to avoid word wrap
if cprof:
cProfile.run(cmd)
else:
profile.run(cmd)
print "</html>"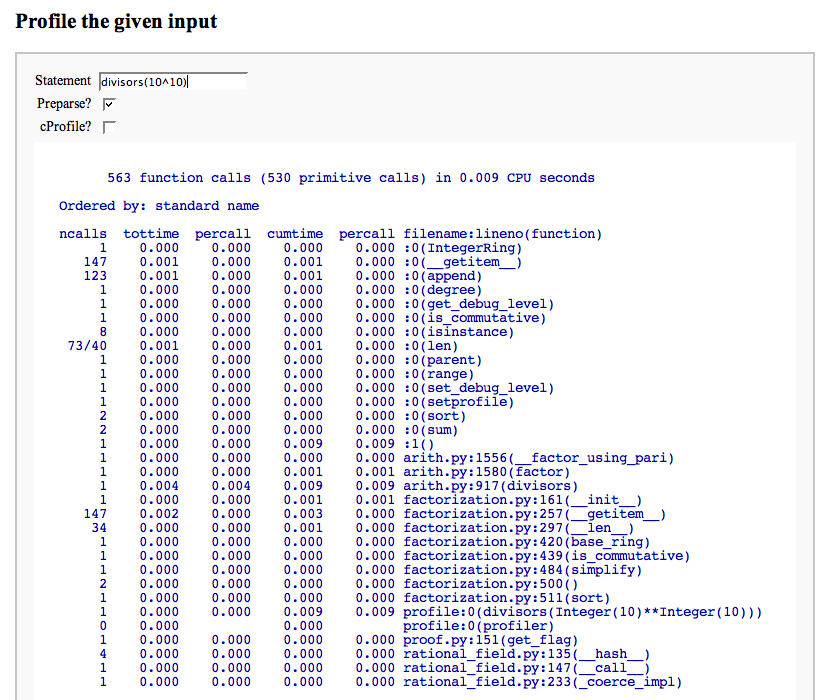
Evaluate a bit of code in a given system
by William Stein (there is no way yet to make the text box big):
@interact
def _(system=selector([('sage0', 'Sage'), ('gp', 'PARI'), ('magma', 'Magma')]), code='2+2'):
print globals()[system].eval(code)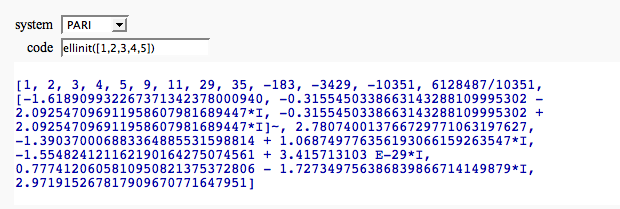
Minkowski Sum
by Marshall Hampton
def minkdemo(list1,list2):
'''
Returns the Minkowski sum of two lists.
'''
output = []
for stuff1 in list1:
for stuff2 in list2:
temp = [stuff1[i] + stuff2[i] for i in range(len(stuff1))]
output.append(temp)
return output
@interact
def minksumvis(x1tri = slider(-1,1,1/10,0, label = 'Triangle point x coord.'), yb = slider(1,4,1/10,2, label = 'Blue point y coord.')):
t_list = [[1,0],[x1tri,1],[0,0]]
kite_list = [[3, 0], [1, 0], [0, 1], [1, yb]]
triangle = polygon([[q[0]-6,q[1]] for q in t_list], alpha = .5, rgbcolor = (1,0,0))
t_vert = point([x1tri-6,1], rgbcolor = (1,0,0))
b_vert = point([kite_list[3][0]-4,yb], rgbcolor = (0,0,1))
kite = polygon([[q[0]-4,q[1]] for q in kite_list], alpha = .5,rgbcolor = (0,0,1))
p12 = minkdemo(t_list, kite_list)
p12 = [[q[0],q[1]] for q in p12]
p12poly = Polyhedron(p12)
edge_lines = Graphics()
verts = p12poly.vertices()
for an_edge in p12poly.vertex_adjacencies():
edge_lines += line([verts[an_edge[0]], verts[an_edge[1][0]]])
edge_lines += line([verts[an_edge[0]], verts[an_edge[1][1]]])
triangle_sum = Graphics()
for vert in kite_list:
temp_list = []
for q in t_list:
temp_list.append([q[i] + vert[i] for i in range(len(t_list[0]))])
triangle_sum += polygon(temp_list, alpha = .5, rgbcolor = (1,0,0))
kite_sum = Graphics()
for vert in t_list:
temp_list = []
for q in kite_list:
temp_list.append([q[i] + vert[i] for i in range(len(t_list[0]))])
kite_sum += polygon(temp_list, alpha = .3,rgbcolor = (0,0,1))
labels = text('+', (-4.3,.5), rgbcolor = (0,0,0))
labels += text('=', (-.2,.5), rgbcolor = (0,0,0))
show(labels + t_vert + b_vert+ triangle + kite + triangle_sum + kite_sum + edge_lines, axes=False, figsize = [11.0*.7, 4*.7], xmin = -6, ymin = 0, ymax = 4)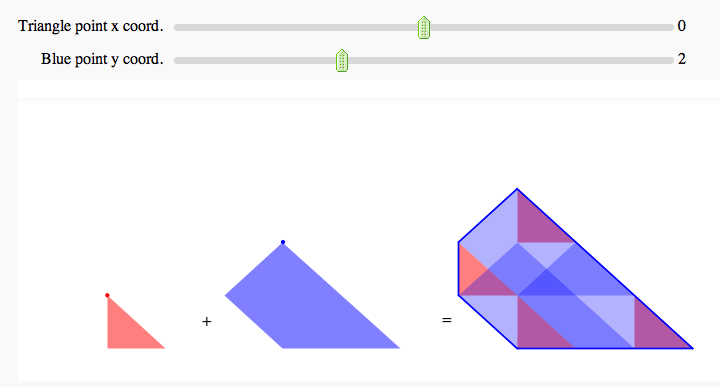
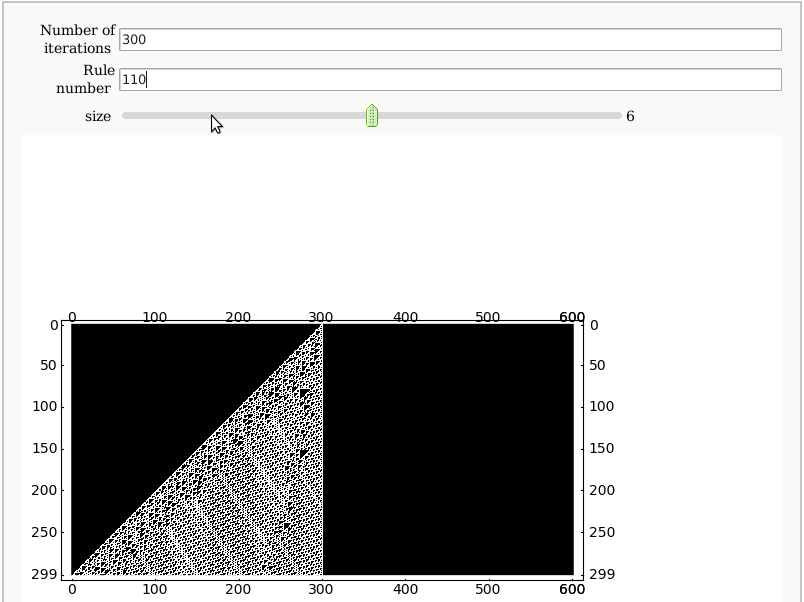
Cellular Automata
by Pablo Angulo, Eviatar Bach
from numpy import zeros
def cellular(rule, N):
'''Yields a matrix showing the evolution of a Wolfram's cellular automaton
rule: determines how a cell's value is updated, depending on its neighbors
N: number of iterations
'''
M=zeros( (N,2*N+1), dtype=int)
M[0,N]=1
for j in range(1,N):
for k in range(0,2*N):
l = 4*M[j-1,k-1] + 2*M[j-1,k] + M[j-1,k+1]
M[j,k]=rule[ l ]
return M[:,:-1]def num2rule(number):
if not 0 <= number <= 255:
raise Exception('Invalid rule number')
binary_digits = number.digits(base=2)
return binary_digits + [0]*(8-len(binary_digits))
@interact
def _( N=input_box(label='Number of iterations',default=100),
rule_number=input_box(label='Rule number',default=110),
size = slider(1, 11, step_size=1, default=6 ) ):
rule = num2rule(rule_number)
M = cellular(rule, N)
plot_M = matrix_plot(M, cmap='binary')
plot_M.show( figsize=[size,size])