Sage Interactions - Linear Algebra
goto interact main page
Contents
Numerical instability of the classical Gram-Schmidt algorithm
by Marshall Hampton (tested by William Stein, who thinks this is really nice!)
def GS_classic(a_list):
'''
Given a list of vectors or a matrix, returns the QR factorization using the classical (and numerically unstable) Gram-Schmidt algorithm.
'''
if type(a_list) != list:
cols = a_list.cols()
a_list = [x for x in cols]
indices = range(len(a_list))
q = []
r = [[0 for i in indices] for j in indices]
v = [a_list[i].copy() for i in indices]
for i in indices:
for j in range(0,i):
r[j][i] = q[j].inner_product(a_list[i])
v[i] = v[i] - r[j][i]*q[j]
r[i][i] = (v[i]*v[i])^(1/2)
q.append(v[i]/r[i][i])
q = matrix([q[i] for i in indices]).transpose()
return q, matrix(r)
def GS_modern(a_list):
'''
Given a list of vectors or a matrix, returns the QR factorization using the 'modern' Gram-Schmidt algorithm.
'''
if type(a_list) != list:
cols = a_list.cols()
a_list = [x for x in cols]
indices = range(len(a_list))
q = []
r = [[0 for i in indices] for j in indices]
v = [a_list[i].copy() for i in indices]
for i in indices:
r[i][i] = v[i].norm(2)
q.append(v[i]/r[i][i])
for j in range(i+1, len(indices)):
r[i][j] = q[i].inner_product(v[j])
v[j] = v[j] - r[i][j]*q[i]
q = matrix([q[i] for i in indices]).transpose()
return q, matrix(r)
html('<h2>Numerical instability of the classical Gram-Schmidt algorithm</h2>')
@interact
def gstest(precision = slider(range(3,53), default = 10), a1 = input_box([1,1/1000,1/1000]), a2 = input_box([1,1/1000,0]), a3 = input_box([1,0,1/1000])):
myR = RealField(precision)
displayR = RealField(5)
html('precision in bits: ' + str(precision) + '<br>')
A = matrix([a1,a2,a3])
A = [vector(myR,x) for x in A]
qn, rn = GS_classic(A)
qb, rb = GS_modern(A)
html('Classical Gram-Schmidt:')
show(matrix(displayR,qn))
html('Stable Gram-Schmidt:')
show(matrix(displayR,qb))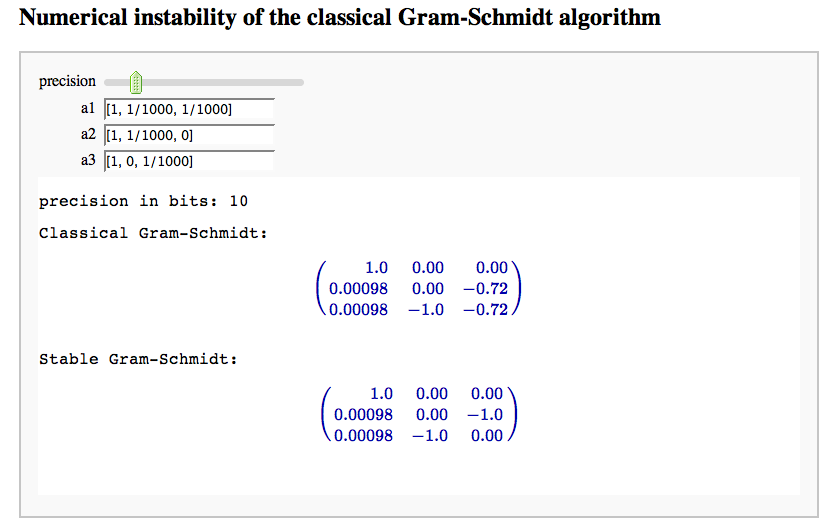
Linear transformations
by Jason Grout
A square matrix defines a linear transformation which rotates and/or scales vectors. In the interact command below, the red vector represents the original vector (v) and the blue vector represents the image w under the linear transformation. You can change the angle and length of v by changing theta and r.
@interact
def linear_transformation(theta=slider(0, 2*pi, .1), r=slider(0.1, 2, .1, default=1)):
A=matrix([[1,-1],[-1,1/2]])
v=vector([r*cos(theta), r*sin(theta)])
w = A*v
circles = sum([circle((0,0), radius=i, rgbcolor=(0,0,0)) for i in [1..2]])
print jsmath("v = %s,\; %s v=%s"%(v.n(4),latex(A),w.n(4)))
show(v.plot(rgbcolor=(1,0,0))+w.plot(rgbcolor=(0,0,1))+circles,aspect_ratio=1)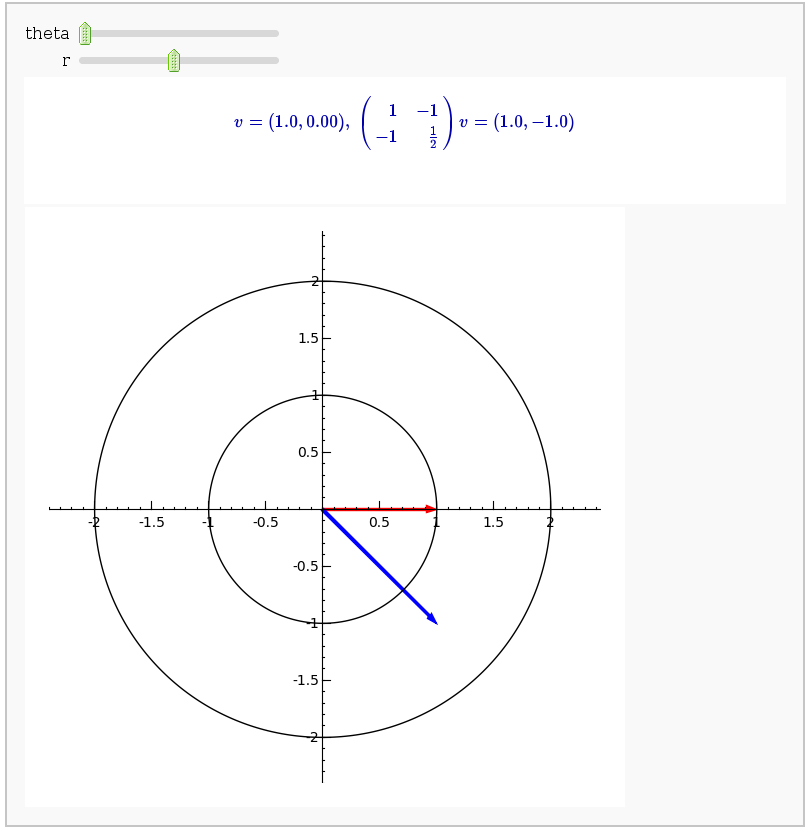
Gerschgorin Circle Theorem
by Marshall Hampton. This animated version requires convert (imagemagick) to be installed, but it can easily be modified to a static version. The animation illustrates the idea behind the stronger version of Gerschgorin's theorem, which says that if the disks around the eigenvalues are disjoint then there is one eigenvalue per disk. The proof is by continuity of the eigenvalues under a homotopy to a diagonal matrix.
from scipy import linalg
html('<h2>The Gerschgorin circle theorem</h2>')
@interact
def Gerschgorin(Ain = input_box(default='[[10,1,1/10,0],[-1,9,0,1],[1,0,2,3/10],[-.5,0,-.3,1]]', type = str, label = 'A = '), an_size = slider(1,100,1,1.0)):
A = sage_eval(Ain)
size = len(A)
print jsmath('A = ' + latex(matrix(RealField(10),A)))
A = matrix(RealField(10),A)
B = [[0 for i in range(size)] for j in range(size)]
for i in range(size):
B[i][i] = A[i][i]
B = matrix(B)
frames = []
centers = [(real(q),imag(q)) for q in [A[i][i] for i in range(size)]]
radii_row = [sum([abs(A[i][j]) for j in range(i)+range(i+1,size)]) for i in range(size)]
radii_col = [sum([abs(A[j][i]) for j in range(i)+range(i+1,size)]) for i in range(size)]
x_min = min([centers[i][0]-radii_row[i] for i in range(size)]+[centers[i][0]-radii_col[i] for i in range(size)])
x_max = max([centers[i][0]+radii_row[i] for i in range(size)]+[centers[i][0]+radii_col[i] for i in range(size)])
y_min = min([centers[i][1]-radii_row[i] for i in range(size)]+[centers[i][1]-radii_col[i] for i in range(size)])
y_max = max([centers[i][1]+radii_row[i] for i in range(size)]+[centers[i][1]+radii_col[i] for i in range(size)])
if an_size > 1:
t_range= srange(0,1+1/an_size,1/an_size)
else:
t_range = [1]
for t in t_range:
C = t*A + (1-t)*B
eigs = [CDF(x) for x in linalg.eigvals(C.numpy())]
eigpoints = points([(real(q),imag(q)) for q in eigs],pointsize = 10, rgbcolor = (0,0,0))
centers = [(real(q),imag(q)) for q in [A[i][i] for i in range(size)]]
radii_row = [sum([abs(C[i][j]) for j in range(i)+range(i+1,size)]) for i in range(size)]
radii_col = [sum([abs(C[j][i]) for j in range(i)+range(i+1,size)]) for i in range(size)]
scale = max([(x_max-x_min),(y_max-y_min)])
scale = 7/scale
row_circles = sum([circle(centers[i],radii_row[i],fill=True, alpha = .3) for i in range(size)])
col_circles = sum([circle(centers[i],radii_col[i],fill=True, rgbcolor = (1,0,0), alpha = .3) for i in range(size)])
ft = eigpoints+row_circles+col_circles
frames.append(ft)
show(animate(frames,figsize = [(x_max-x_min)*scale,(y_max-y_min)*scale], xmin = x_min, xmax=x_max, ymin = y_min, ymax = y_max))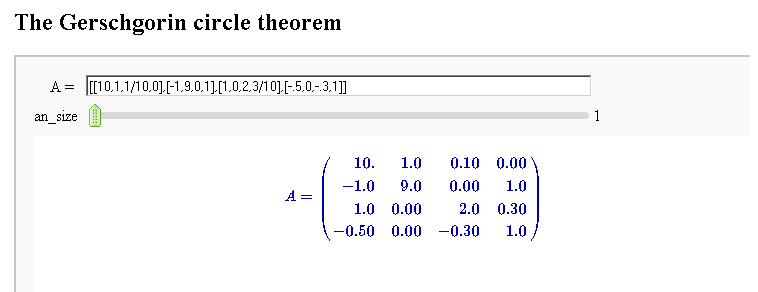
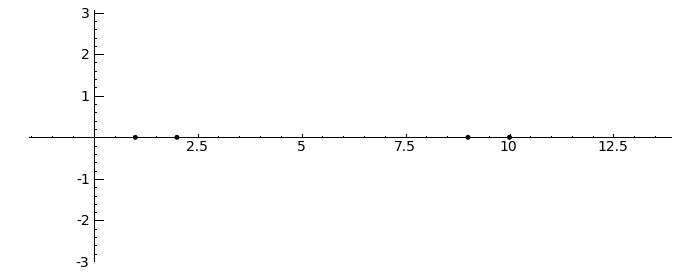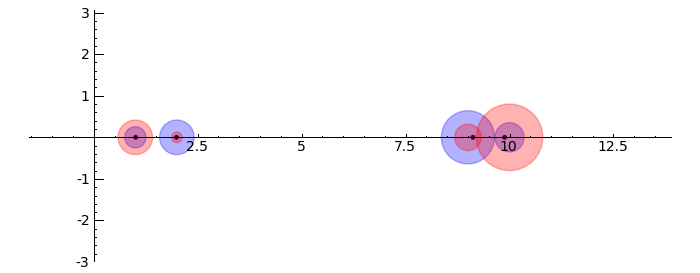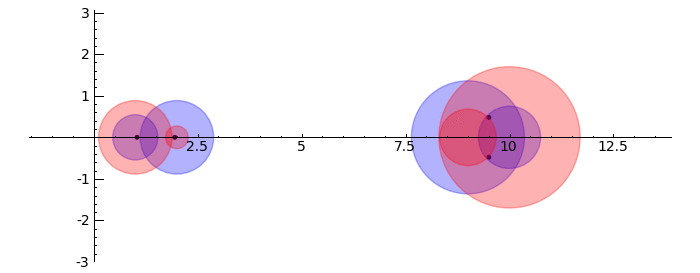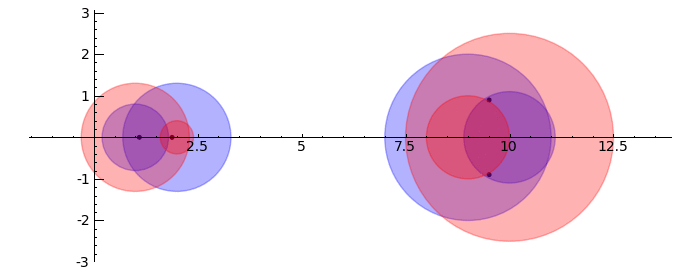
Singular value decomposition
by Marshall Hampton
import scipy.linalg as lin
var('t')
def rotell(sig,umat,t,offset=0):
temp = matrix(umat)*matrix(2,1,[sig[0]*cos(t),sig[1]*sin(t)])
return [offset+temp[0][0],temp[1][0]]
@interact
def svd_vis(a11=slider(-1,1,.05,1),a12=slider(-1,1,.05,1),a21=slider(-1,1,.05,0),a22=slider(-1,1,.05,1),ofs= selector(['Off','On'],label='offset image from domain')):
rf_low = RealField(12)
my_mat = matrix(rf_low,2,2,[a11,a12,a21,a22])
u,s,vh = lin.svd(my_mat.numpy())
if ofs == 'On':
offset = 3
fsize = 6
colors = [(1,0,0),(0,0,1),(1,0,0),(0,0,1)]
else:
offset = 0
fsize = 5
colors = [(1,0,0),(0,0,1),(.7,.2,0),(0,.3,.7)]
vvects = sum([arrow([0,0],matrix(vh).row(i),rgbcolor = colors[i]) for i in (0,1)])
uvects = Graphics()
for i in (0,1):
if s[i] != 0: uvects += arrow([offset,0],vector([offset,0])+matrix(s*u).column(i),rgbcolor = colors[i+2])
html('<h3>Singular value decomposition: image of the unit circle and the singular vectors</h3>')
print jsmath("A = %s = %s %s %s"%(latex(my_mat), latex(matrix(rf_low,u.tolist())), latex(matrix(rf_low,2,2,[s[0],0,0,s[1]])), latex(matrix(rf_low,vh.tolist()))))
image_ell = parametric_plot(rotell(s,u,t, offset),0,2*pi)
graph_stuff=circle((0,0),1)+image_ell+vvects+uvects
graph_stuff.set_aspect_ratio(1)
show(graph_stuff,frame = False,axes=False,figsize=[fsize,fsize])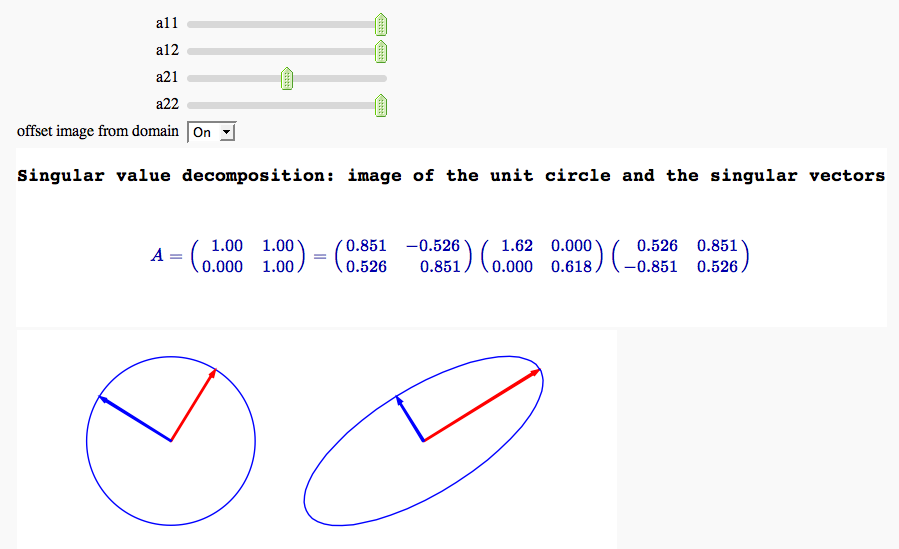
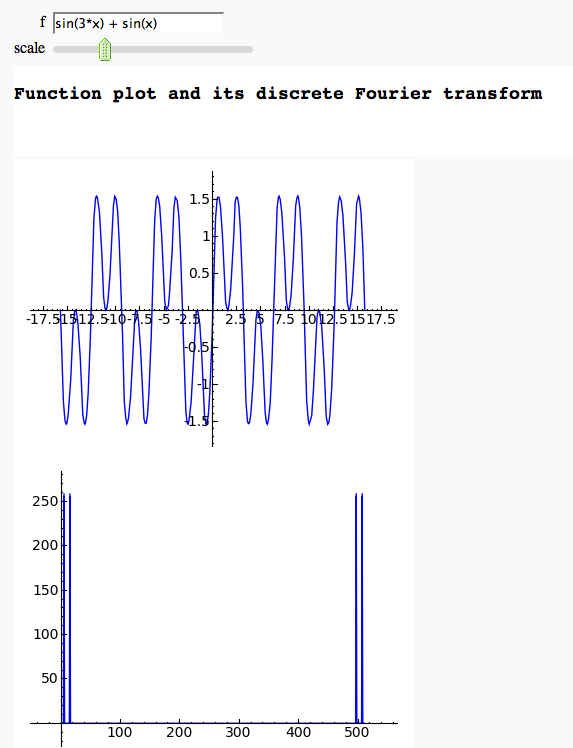
Discrete Fourier Transform
by Marshall Hampton
import scipy.fftpack as Fourier
@interact
def discrete_fourier(f = input_box(default=sum([sin(k*x) for k in range(1,5,2)])), scale = slider(.1,20,.1,5)):
var('x')
pbegin = -float(pi)*scale
pend = float(pi)*scale
html("<h3>Function plot and its discrete Fourier transform</h3>")
show(plot(f, pbegin, pend, plot_points = 512), figsize = [4,3])
f_vals = [f(ind) for ind in srange(pbegin, pend,(pend-pbegin)/512.0)]
my_fft = Fourier.fft(f_vals)
show(list_plot([abs(x) for x in my_fft], plotjoined=True), figsize = [4,3])