|
Size: 7466
Comment: added figures
|
Size: 7528
Comment: translated a couple of sentences into english, but left names like tiempo to keep the builtin time alone
|
| Deletions are marked like this. | Additions are marked like this. |
| Line 155: | Line 155: |
| def _(tiempo=(0.1*j for j in (0..10))): ft=sum(a*sin(x*n/2)*exp(-k*(n/2)^2*tiempo) for n,a in alpha) pt = plot(ft,0, 2*pi, color='green', thickness=2) show(p + pt, ymin = -.2) |
def _(tiempo = (0.1*j for j in (0..10)) ): ft = sum( a*sin(x*n/2)*exp(-k*(n/2)^2*tiempo) for n,a in alpha) pt = plot(ft, 0, 2*pi, color='green', thickness=2) show( p + pt, ymin = -.2) |
| Line 167: | Line 167: |
| #cython code implementing a very simple finite diference scheme | |
| Line 174: | Line 175: |
| s=k*dt/(dx**2) #tenemos que sustituir ^ por ** para exponenciar | s=k*dt/(dx**2) #we cannot use ^ for exponentiation in cython |
| Line 181: | Line 182: |
| #Versión interactiva usando el código cython | #interact box wrapping the code above |
| Line 195: | Line 196: |
| print 's=%f > 1/2!!! El metodo no es estable'%s | print 's=%f > 1/2!!! The method is not stable'%s |
Sage Interactions - Differential Equations
goto interact main page
Contents
Euler's Method in one variable
by Marshall Hampton. This needs some polishing but its usable as is.
def tab_list(y, headers = None):
'''
Converts a list into an html table with borders.
'''
s = '<table border = 1>'
if headers:
for q in headers:
s = s + '<th>' + str(q) + '</th>'
for x in y:
s = s + '<tr>'
for q in x:
s = s + '<td>' + str(q) + '</td>'
s = s + '</tr>'
s = s + '</table>'
return s
var('x y')
@interact
def euler_method(y_exact_in = input_box('-cos(x)+1.0', type = str, label = 'Exact solution = '), y_prime_in = input_box('sin(x)', type = str, label = "y' = "), start = input_box(0.0, label = 'x starting value: '), stop = input_box(6.0, label = 'x stopping value: '), startval = input_box(0.0, label = 'y starting value: '), nsteps = slider([2^m for m in range(0,10)], default = 10, label = 'Number of steps: '), show_steps = slider([2^m for m in range(0,10)], default = 8, label = 'Number of steps shown in table: ')):
y_exact = lambda x: eval(y_exact_in)
y_prime = lambda x,y: eval(y_prime_in)
stepsize = float((stop-start)/nsteps)
steps_shown = max(nsteps,show_steps)
sol = [startval]
xvals = [start]
for step in range(nsteps):
sol.append(sol[-1] + stepsize*y_prime(xvals[-1],sol[-1]))
xvals.append(xvals[-1] + stepsize)
sol_max = max(sol + [find_maximum_on_interval(y_exact,start,stop)[0]])
sol_min = min(sol + [find_minimum_on_interval(y_exact,start,stop)[0]])
show(plot(y_exact(x),start,stop,rgbcolor=(1,0,0))+line([[xvals[index],sol[index]] for index in range(len(sol))]),xmin=start,xmax = stop, ymax = sol_max, ymin = sol_min)
if nsteps < steps_shown:
table_range = range(len(sol))
else:
table_range = range(0,floor(steps_shown/2)) + range(len(sol)-floor(steps_shown/2),len(sol))
html(tab_list([[i,xvals[i],sol[i]] for i in table_range], headers = ['step','x','y']))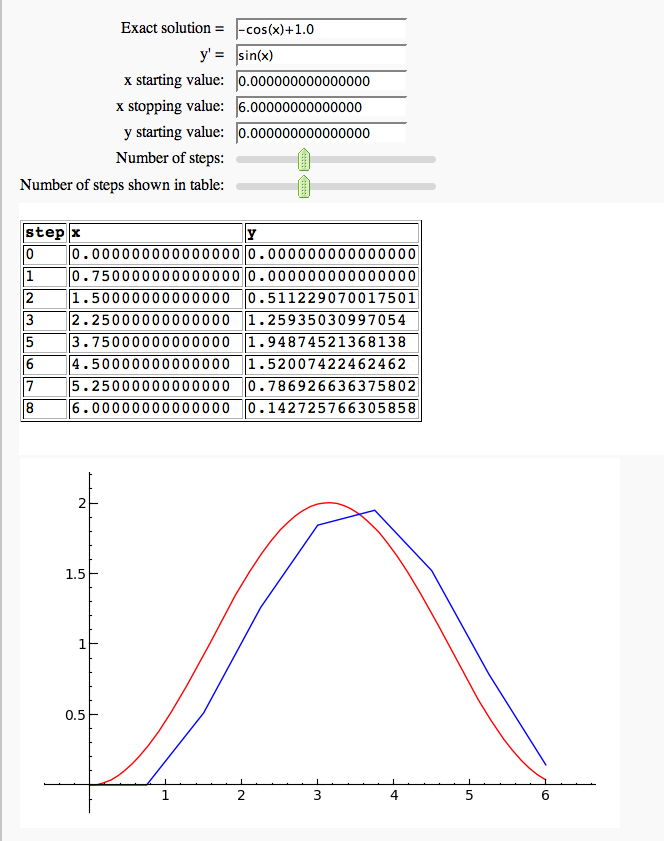
Vector Fields and Euler's Method
by Mike Hansen (tested and updated by William Stein)
x,y = var('x,y')
@interact
def _(f = input_box(default=y), g=input_box(default=-x*y+x^3-x),
xmin=input_box(default=-1), xmax=input_box(default=1),
ymin=input_box(default=-1), ymax=input_box(default=1),
start_x=input_box(default=0.5), start_y=input_box(default=0.5),
step_size=(0.01,(0.001, 0.2)), steps=(600,(0, 1400)) ):
old_f = f
f = f.function(x,y)
old_g = g
g = g.function(x,y)
steps = int(steps)
points = [ (start_x, start_y) ]
for i in range(steps):
xx, yy = points[-1]
try:
points.append( (xx+step_size*f(xx,yy), yy+step_size*g(xx,yy)) )
except (ValueError, ArithmeticError, TypeError):
break
starting_point = point(points[0], pointsize=50)
solution = line(points)
vector_field = plot_vector_field( (f,g), (x,xmin,xmax), (y,ymin,ymax) )
result = vector_field + starting_point + solution
html(r"<h2>$ \frac{dx}{dt} = %s$ $ \frac{dy}{dt} = %s$</h2>"%(latex(old_f),latex(old_g)))
print "Step size: %s"%step_size
print "Steps: %s"%steps
result.show(xmin=xmin,xmax=xmax,ymin=ymin,ymax=ymax)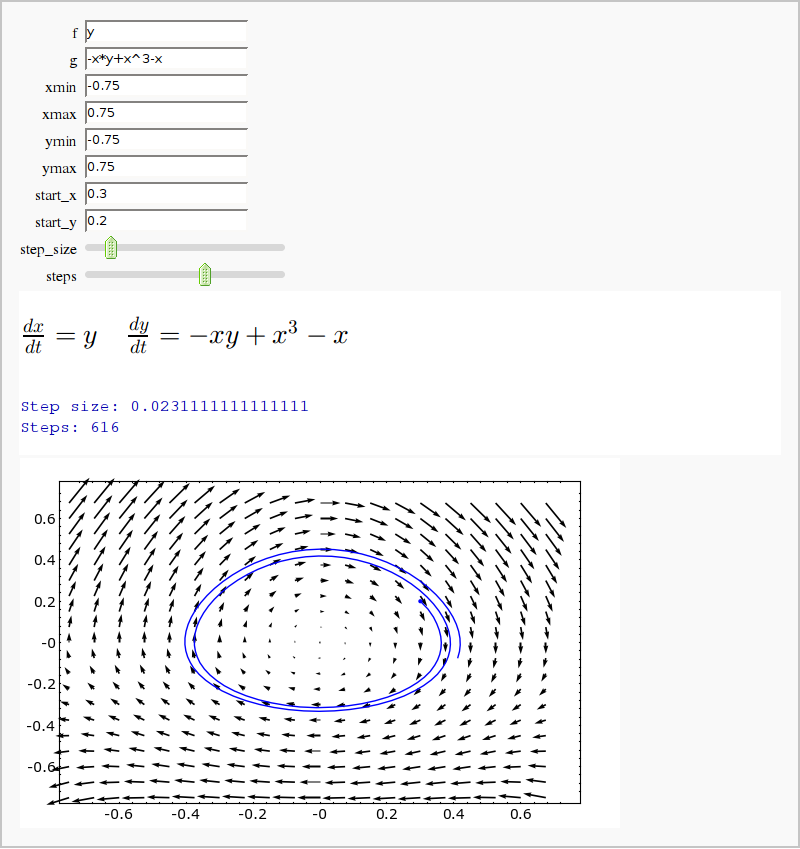
Vector Field with Runga-Kutta-Fehlberg
by Harald Schilly
# Solve ODEs using sophisticated Methods like Runga-Kutta-Fehlberg
# by Harald Schilly, April 2008
# (jacobian doesn't work, please fix ...)
var('x y')
@interact
def _(fin = input_box(default=y+exp(x/10)-1/3*((x-1/2)^2+y^3)*x-x*y^3), gin=input_box(default=x^3-x+1/100*exp(y*x^2+x*y^2)-0.7*x),
xmin=input_box(default=-1), xmax=input_box(default=1.8),
ymin=input_box(default=-1.3), ymax=input_box(default=1.5),
x_start=(-1,(-2,2)), y_start=(0,(-2,2)), error=(0.5,(0,1)),
t_length=(23,(0, 100)) , num_of_points = (1500,(5,2000)),
algorithm = selector([
("rkf45" , "runga-kutta-felhberg (4,5)"),
("rk2" , "embedded runga-kutta (2,3)"),
("rk4" , "4th order classical runga-kutta"),
("rk8pd" , 'runga-kutta prince-dormand (8,9)'),
("rk2imp" , "implicit 2nd order runga-kutta at gaussian points"),
("rk4imp" , "implicit 4th order runga-kutta at gaussian points"),
("bsimp" , "implicit burlisch-stoer (requires jacobian)"),
("gear1" , "M=1 implicit gear"),
("gear2" , "M=2 implicit gear")
])):
f(x,y)=fin
g(x,y)=gin
ff = f._fast_float_(*f.args())
gg = g._fast_float_(*g.args())
#solve
path = []
err = error
xerr = 0
for yerr in [-err, 0, +err]:
T=ode_solver()
T.algorithm=algorithm
T.function = lambda t, yp: [ff(yp[0],yp[1]), gg(yp[0],yp[1])]
T.jacobian = lambda t, yp: [[diff(fun,dval)(yp[0],yp[1]) for dval in [x,y]] for fun in [f,g]]
T.ode_solve(y_0=[x_start + xerr, y_start + yerr],t_span=[0,t_length],num_points=num_of_points)
path.append(line([p[1] for p in T.solution]))
#plot
vector_field = plot_vector_field( (f,g), (x,xmin,xmax), (y,ymin,ymax) )
starting_point = point([x_start, y_start], pointsize=50)
show(vector_field + starting_point + sum(path), aspect_ratio=1, figsize=[8,9])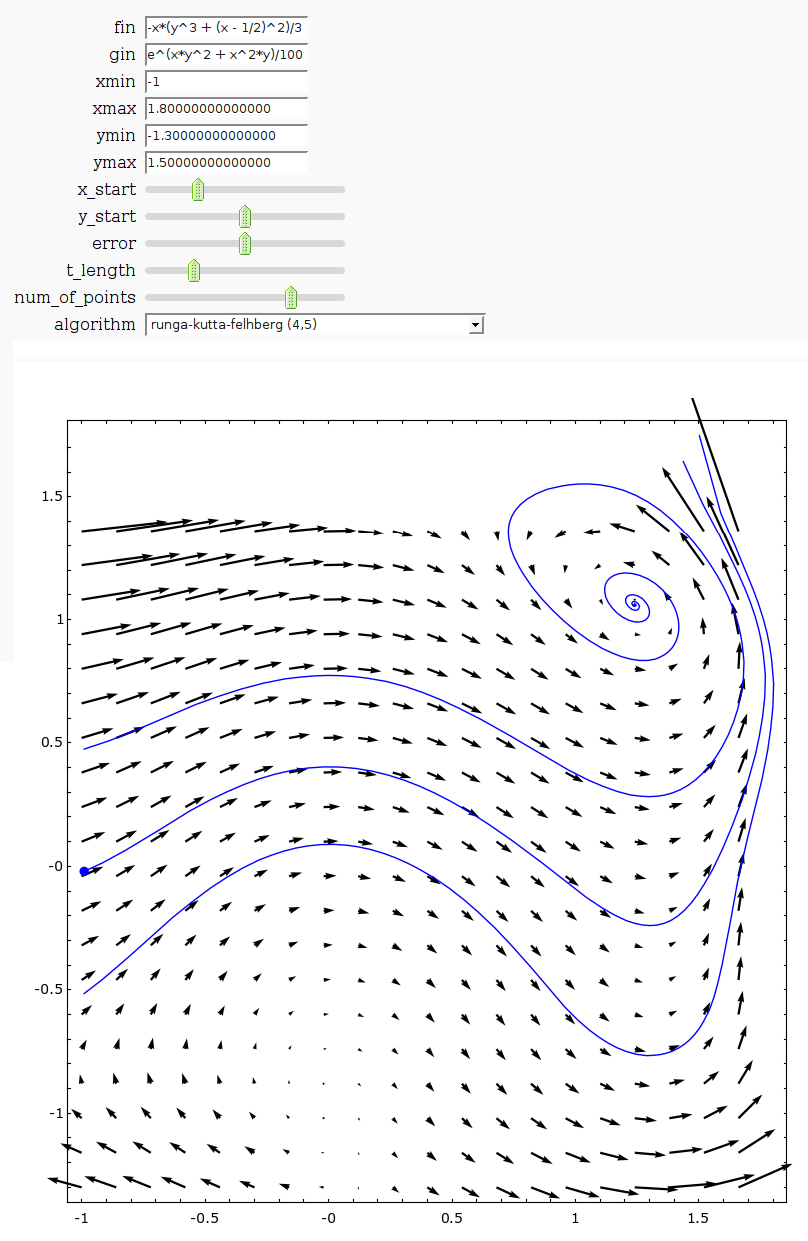
Mass/Spring systems
by Jason Grout
These two interacts involve some Cython code or other scipy imports, so I've posted a file containing them. You can download the worksheet or copy it online.
Heat equation using Fourier series
by Pablo Angulo
var('x')
x0 = 0
k=1
f = x*exp(-x^2)
p = plot(f,0,2*pi, thickness=2)
c = 1/pi
orden=10
alpha=[(n,c*numerical_integral(f(x)*sin(x*n/2),0,2*pi)[0] ) for n in range(1,orden)]
@interact
def _(tiempo = (0.1*j for j in (0..10)) ):
ft = sum( a*sin(x*n/2)*exp(-k*(n/2)^2*tiempo) for n,a in alpha)
pt = plot(ft, 0, 2*pi, color='green', thickness=2)
show( p + pt, ymin = -.2)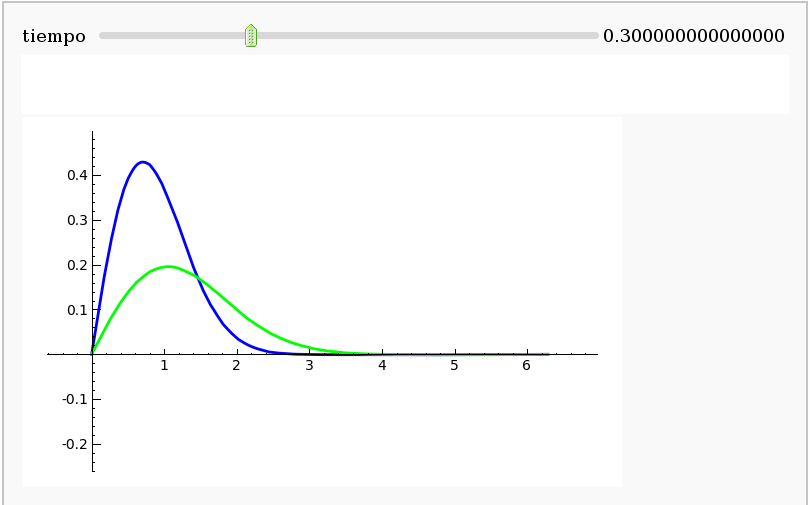
Heat equation using finite diferences in cython (very fast!)
by Pablo Angulo
%cython
#cython code implementing a very simple finite diference scheme
import numpy as np
def calor_cython(u0,float dx, float k,float t_f,int tsteps):
cdef int m
cdef float dt
cdef float s
u=np.array(u0)
dt=t_f/tsteps
s=k*dt/(dx**2) #we cannot use ^ for exponentiation in cython
for m in range(tsteps):
u[1:-1]=(1-2*s)*u[1:-1]+s*u[0:-2]+s*u[2:]
return u#interact box wrapping the code above
var('x')
@interact
def _(f=input_box(default=x*exp(-x^2)), longitud=input_box(default=2*pi),
tiempo=input_box(default=0.1), M=input_box(default=100),
k=input_box(default=1), tsteps=input_box(default=2000) ):
efe=f._fast_float_()
dx=float(longitud/M)
xs=[n*dx for n in range(M+1)]
u0=[efe(a) for a in xs]
s=k*(tiempo/tsteps) /dx^2
if s>0.5:
print 's=%f > 1/2!!! The method is not stable'%s
ut=calor_cython(u0,dx,k,tiempo,tsteps)
show( line2d(zip(xs, u0)) + line2d(zip(xs, ut), rgbcolor='green') )
