|
Size: 1361
Comment: add link to metaticket
|
Size: 60508
Comment: link changelog
|
| Deletions are marked like this. | Additions are marked like this. |
| Line 3: | Line 3: |
| in planning (2020) | released October 24, 2020 |
| Line 7: | Line 7: |
| == Python 3 transition == SageMath 9.0 was the first version of Sage running on Python 3 by default. Sage 9.1 continues to support Python 2. Sage 9.2 will remove support for Python 2. See [[Python3-Switch]] for more details [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/29141|Meta-ticket #29141: Upgrades and other changes that require dropping py2 support]] |
== Python 3 transition completed == [[ReleaseTours/sage-9.0|SageMath 9.0]] was the first version of Sage running on Python 3 by default. [[ReleaseTours/sage-9.1|SageMath 9.1]] continued to support Python 2. === Support for Python 2 removed === Sage 9.2 has removed support for Python 2. The Sage library now makes use of Python language and library features that are only available in Python 3.6 or newer; and large amounts of compatibility code have been removed. However, note that this is unrelated to the minimal requirements for a source installation of the Sage distribution: Sage 9.2 is still able to build on a system that only provides Python 2.x or Python 3.5 or older. In this case, the SageMath distribution builds its own copy of Python 3. === Support for Python 3.6, 3.8, and 3.9 added === Sage 9.2 has added support for Python 3.8 in [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/27754|#27754]] and Python 3.9 in [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/30184|#30184]]. Sage 9.2 has also added support for Python 3.6. This allows Sage to use the system Python on some older Linux distributions that are still in widespread use in scientific computing, including `centos-8` and `fedora-{26,27,28}` (although Python 3.7.x packages are also available for these). See [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/29033|#29033]] for more details. Hence, Sage 9.2 conforms to (and exceeds) [[https://numpy.org/neps/nep-0029-deprecation_policy.html|NumPy Enhancement Proposal 29]] regarding Python version support policies. If no suitable system Python, versions 3.6.x, 3.7.x, 3.8.x, or 3.9.x is found, Sage installs its own copy of Python 3 from source. The version of Python shipped with the Sage distribution has been upgraded from 3.7.3 to 3.8.5. === For developers: Using Python 3.6+ features in sagelib === [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/29756|Meta-ticket #29756]] provides a starting point for a discussion of new features of the Python language and standard library to bring them to systematic use in sagelib. All features provided by Python 3.6 can be used immediately; features introduced in Python 3.7 or later will require backporting or a decision to drop the goal of supporting Python 3.6. === More details === * [[https://trac.sagemath.org/query?keywords=~python3&milestone=sage-9.2&or&component=python3&milestone=sage-9.2&or&keywords=~py3&milestone=sage-9.2&groupdesc=1&group=status&max=1500&col=id&col=summary&col=keywords&col=component&col=time&col=changetime&col=author&col=reviewer&order=component|Trac tickets with keyword/component python3 in milestone 9.2]] * See [[Python3-Switch]] for more details. == Package upgrades == The removal of support for Python 2 has enabled major package upgrades. Major user-visible package upgrades below... === matplotlib === Dropping Python 2 support allowed us to make a major jump from matplotlib 2.2.5 to 3.3.1. See matplotlib's [[https://matplotlib.org/3.3.0/users/prev_whats_new/whats_new_3.0.html|release notes for 3.0]], [[https://matplotlib.org/3.3.0/users/prev_whats_new/whats_new_3.1.0.html|3.1]], [[https://matplotlib.org/3.3.0/users/prev_whats_new/whats_new_3.2.0.html|3.2]],[[https://matplotlib.org/3.3.0/users/prev_whats_new/whats_new_3.3.0.html|3.3]]. In addition to improved output, this update will likely enable Sage developers to implement new features for plotting and graphics. === rpy2 and R === The [[https://pypi.org/project/rpy2/|rpy2 Python package]] is the foundation for [[https://doc.sagemath.org/html/en/reference/interfaces/sage/interfaces/r.html|SageMath's interface]] to [[https://www.r-project.org/|R]]. Dropping Python 2 support allowed us to make the major upgrade from 2.8.2 to 3.3.5 in [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/29441|#29441]]; see the [[https://rpy2.github.io/doc/latest/html/changes.html#release-3-3-1|release notes]] for details. We only did a minor upgrade of R itself in the Sage distribution, to 3.6.3, the latest in the 3.6.x series. Of course, if R 4.0.x is installed in the system, Sage will use it instead of building its own copy. The SageMath developers are eager to learn from users how they use the SageMath-R interface, and what needs to be added to it to become more powerful. Let us know at [[https://groups.google.com/d/msg/sage-devel|sage-devel]]. === sphinx === Sage uses [[https://www.sphinx-doc.org/en/master/|Sphinx]] to build its [[https://doc.sagemath.org/html/en/index.html|documentation]]. Sage 9.2 has updated Sphinx from 1.8.5 to 3.1.2; see [[https://www.sphinx-doc.org/en/master/changes.html#release-3-1-2-released-jul-05-2020|Sphinx release notes]] for more information. === SymPy === [[https://www.sympy.org/en/index.html|SymPy]] has been updated from 1.5 to 1.6.2 in [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/29730|#29730]], [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/30425|#30425]]. See the [[https://github.com/sympy/sympy/wiki/Release-Notes|Release notes]]. === IPython, Jupyter notebook, JupyterLab === Dropping support for Python 2 allowed us to upgrade IPython from 5.8.0 to 7.13.0 in [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/28197|#28197]]. See the [[https://ipython.readthedocs.io/en/stable/whatsnew/version6.html|release notes for the 6.x]] and [[https://ipython.readthedocs.io/en/stable/whatsnew/version7.html|7.x series]]. We have also upgraded the Jupyter notebook from 5.7.6 to 6.1.1 in [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/26919|#26919]]; see the [[https://jupyter-notebook.readthedocs.io/en/stable/changelog.html|notebook changelog]] for more information. Besides, the pdf export of Jupyter notebooks has been fixed, so that LaTeX-typeset outputs are now rendered in the pdf file ([[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/23330|#23330]]). [[https://jupyterlab.readthedocs.io/en/stable/|JupyterLab]] is now fully supported as an optional, alternative interface [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/30246|#30246]], including [[https://doc.sagemath.org/html/en/prep/Quickstarts/Interact.html|interacts]]. To use it, install it first, using the command `sage -i jupyterlab_widgets`. Then you can start it using `./sage -n jupyterlab`. === Normaliz === The optional package [[https://www.normaliz.uni-osnabrueck.de/|Normaliz]], a tool for computations in affine monoids, vector configurations, lattice polytopes, rational cones, and algebraic polyhedra has been upgraded from 3.7.2 to 3.8.8, and !PyNormaliz to version 2.12. The upgrade [[https://github.com/Normaliz/Normaliz/releases|adds]] support for incremental ("dynamic") computations, the computation of automorphism groups and refined triangulations of cones and polyhedra, and limited support for semiopen cones and polyhedra. To install Normaliz and !PyNormaliz, use `sage -i pynormaliz`. === SageTeX === [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/30342|Updated to version 3.5]], improving Python 3 compatibility, also updated to version 3.5 on [[https://ctan.org|CTAN]]. === Other package updates === * [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/29141|Meta-ticket #29141: Upgrades and other changes that require dropping py2 support]] * [[https://trac.sagemath.org/query?summary=~update&milestone=sage-9.2&or&milestone=sage-9.2&summary=~upgrade&groupdesc=1&group=status&max=1500&col=id&col=summary&col=component&col=time&col=changetime&col=author&col=reviewer&col=keywords&order=component|Upgrade tickets, milestone 9.2]] === For developers: Upgrading packages === Upgrading Python packages in the Sage distribution from PyPI has again become easier, thanks to [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/20104|#20104]]. You can now do: {{{ $ sage --package update-latest matplotlib Updating matplotlib: 3.3.0 -> 3.3.1 Downloading tarball to ...matplotlib-3.3.1.tar.bz2 [...............................................................] }}} When you do this, please remember to check that the `checksums.ini` file has an `upstream_url` in the format `upstream_url=https://pypi.io/packages/source/m/matplotlib/matplotlib-VERSION.tar.gz`. (This is not needed for `updated-latest` to work, but helps with automated tests of the upgrade ticket -- see [[https://wiki.sagemath.org/ReleaseTours/sage-9.1#For_developers-1|Sage 9.1 release tour]] on this topic.) === For packagers: Changes to packages === The packages `giacpy_sage` and `sage_brial` have been merged into `sagelib` as `sage.libs.giac` and `sage.rings.polynomial.pbori`. The directory `build/pkgs/sage_sws2rst/src` contains a new pip-installable package, providing the script `sage-sws2rst`. The Sage library is now built out of the directory `build/pkgs/sagelib/src/`. A pip-installable source distribution (sdist) can be built using the script `build/pkgs/sagelib/spkg-src` ([[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/29411|#29411]], [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/29950|#29950]]). The scripts in `src/bin/` are now installed by sagelib's `setup.py` ([[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/21559|#21559]]). Also several scripts have been moved to `build/bin/`, and some obsolete scripts have been removed ([[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/29825|#29825]], [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/27171|#27171]]). Many build-related functions of the main Sage script, `src/bin/sage` (installed as `sage`), have been moved to a script `build/bin/sage-site` (not installed) in [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/29111|#29111]]. It is hoped that downstream distribution packaging is able to use this cleaned up script instead of replacing it with an ad-hoc distribution-specific script -- so that users can rely on a consistent interface. Contributions of further clean ups and refactoring of the script are welcome. == Graphics == === New features === * Specify the rectangle in which to draw a matrix using the new `xrange` and `yrange` options of `matrix_plot`. For example, to draw a matrix in [0,1]×[0,1] instead of the default [-0.5,4.5]×[-0.5,4.5]: `matrix_plot(identity_matrix(5), xrange=(0, 1), yrange=(0, 1))`. [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/27895|27895]] (Markus Wageringel) * Set the initial camera orientation in Three.js plots using the new `viewpoint` option. Pass it a list/tuple of the form `[[x,y,z],angle]`, such as that provided by the existing `Get Viewpoint` option accessible from the menu button in the lower-right corner of a Three.js plot. [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/29192|29192]] (Paul Masson) * Change the size, font, and opacity of text displayed in the Three.js viewer. For example: {{{ #!python text3d("Hello world!", (0, 0, 0), fontfamily='Times New Roman', fontsize=20, fontweight='bold', fontstyle='italic', opacity=0.5) }}} [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/30614|30614]] (Joshua Campbell) * Save a 3D graphics object directly to an HTML file that uses the Three.js viewer, similar to how you would save a PNG image: `G.save('plot.html')`. [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/29194|29194]] (Joshua Campbell) * Produce an interactive 3D animation that you can pan, rotate, and zoom while the animation is playing using the Three.js viewer. A slider and buttons for controlling playback are included on the page by default. To use this new feature construct an animation as you normally would, passing a list of still frames to the `animate` function, then call the `interactive` method. For example: {{{ #!python def build_frame(t): """Build a single frame of animation at time t.""" e = parametric_plot3d([sin(x-t), 0, x], (x, 0, 2*pi), color='red') b = parametric_plot3d([0, -sin(x-t), x], (x, 0, 2*pi), color='green') return e + b frames = [build_frame(t) for t in (0, pi/32, pi/16, .., 2*pi)] animate(frames, delay=5).interactive( projection='orthographic') }}} [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/29194|29194]] (Joshua Campbell) === Implementation improvements === * Points are now sampled exponentially when `scale='semilogx'` or `scale='loglog'` is specified. This decreases the number of points necessary for an accurate plot (and also increases the chance that the default number of points will produce an acceptable plot). [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/29523|29523]] (Blair Mason) * Points and lines are now ignored in STL 3D export. Moreover disjoint union of surfaces can be saved. [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/29732|29732]] (Frédéric Chapoton) * Three.js has been upgraded to version r117. [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/29809|29809]] (Paul Masson) * Long text is no longer clipped in Three.js plots. Multi-line text is not yet supported but is in the works. [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/29758|29758]] (Joshua Campbell) * JSmol's telemetry functionality has been disabled. It will no longer phone home when, for example, using `viewer='jmol'` in a Jupyter notebook. [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/30030|30030]] (Joshua Campbell) * SVG export has been added to the javascript graph display tool: {{{G.show(method='js')}}} [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/29807|29807]] === For developers === * Clarified that example Three.js plots in the documentation should use the `online=True` viewing option. [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/30136|30136]] (Paul Masson) == Linear and multilinear algebra == === One free module constructor to rule them all === Sage has several specialized implementation classes for free modules and vector spaces. The factory functions `FreeModule` and `VectorSpace` select the appropriate class depending on the base ring and other parameters: {{{ #!python sage: FreeModule(ZZ, 10) Ambient free module of rank 10 over the principal ideal domain Integer Ring sage: FreeModule(FiniteField(5), 10) Vector space of dimension 10 over Finite Field of size 5 sage: QQ^10 is VectorSpace(QQ, 10) True }}} The free modules (vector spaces) created here have a distinguished standard basis indexed by `range(rank)`. In Sage 9.2, these factory functions have been extended in [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/30194|#30194]] so that they cover two more cases: 1. If a sequence or family of indices is passed instead of the rank (dimension), then a [[https://doc.sagemath.org/html/en/reference/combinat/sage/combinat/free_module.html#sage.combinat.free_module.CombinatorialFreeModule|CombinatorialFreeModule]] is created instead. These modules underly SageMath's facilities for [[https://doc.sagemath.org/html/en/reference/combinat/sage/combinat/__init__.html|algebraic combinatorics]]. {{{ #!python sage: U = FreeModule(AA, ['x', 'y', 'z']); U Free module generated by {'x', 'y', 'z'} over Algebraic Real Field sage: V = VectorSpace(QQ, ZZ); V sage: V.basis() Lazy family (Term map from Integer Ring to Free module generated by Integer Ring over Rational Field(i)) _{i in Integer Ring} sage: QQ^SymmetricGroup(4) Free module generated by Symmetric group of order 4! as a permutation group over Rational Field }}} 2. If the factory function is invoked with the parameter `with_basis=None`, then a free module of the given rank ''without'' distinguished basis is created. {{{ #!python sage: W = FreeModule(AA, 3, with_basis=None); W 3-dimensional vector space over the Algebraic Real Field sage: W.category() Category of finite dimensional vector spaces over Algebraic Real Field sage: W.tensor_module(2, 2) Free module of type-(2,2) tensors on the 3-dimensional vector space over the Algebraic Real Field }}} It is represented by an instance of the class [[https://doc.sagemath.org/html/en/reference/tensor_free_modules/|FiniteRankFreeModule]] from `sage.tensor.modules`. These modules are the foundation for the multilinear algebra developed by the !SageManifolds project. === Connecting FiniteRankFreeModule and free modules with distinguished basis === Given a basis of a `FiniteRankFreeModule`, the new method `isomorphism_with_fixed_basis` ([[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/30094|#30094]]) constructs an isomorphism from the `FiniteRankFreeModule` to a free module in the category `ModulesWithBasis`. By default, it uses a `CombinatorialFreeModule`: {{{ #!python sage: V = FiniteRankFreeModule(QQ, 3, start_index=1); V 3-dimensional vector space over the Rational Field sage: basis = e = V.basis("e"); basis Basis (e_1,e_2,e_3) on the 3-dimensional vector space over the Rational Field sage: phi_e = V.isomorphism_with_fixed_basis(basis); phi_e Generic morphism: From: 3-dimensional vector space over the Rational Field To: Free module generated by {1, 2, 3} over Rational Field sage: phi_e(e[1] + 2 * e[2]) e[1] + 2*e[2] }}} === Eigenvalues and eigenvectors === * Experimental functions for computing eigenvalues and eigenvectors in arbitrary precision (via [[http://arblib.org/acb_mat.html#eigenvalues-and-eigenvectors|Arb]]) including error bounds have been added. [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/30393|#30393]] {{{ sage: from sage.matrix.benchmark import hilbert_matrix sage: mat = hilbert_matrix(3).change_ring(CBF) sage: mat.eigenvalues() [[1.40831892712365 +/- 7.16e-15] + [+/- 2.02e-15]*I, [0.12232706585391 +/- 6.49e-15] + [+/- 2.02e-15]*I, [0.00268734035577 +/- 5.60e-15] + [+/- 2.02e-15]*I] }}} * Solving [[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Eigendecomposition_of_a_matrix#Generalized_eigenvalue_problem|generalized eigenvalue problems]] `Av = λBv` for two square matrices `A`, `B` over `RDF` or `CDF` is now supported (via [[https://docs.scipy.org/doc/scipy/reference/generated/scipy.linalg.eig.html|SciPy]]) [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/29243|#29243]]. A generalized eigenvalue `λ` is defined to be a root of the polynomial `det(A - λ B)` if this polynomial is not constantly zero. {{{ sage: A = matrix.identity(RDF, 2) sage: B = matrix(RDF, [[3, 5], [6, 10]]) sage: D, V = A.eigenmatrix_right(B); D # tol 1e-14 [0.07692307692307694 0.0] [ 0.0 +infinity] sage: λ = D[0, 0] sage: v = V[:, 0] sage: (A * v - B * v * λ).norm() < 1e-14 True sage: A.eigenvalues(B, homogeneous=True) [(0.9999999999999999, 13.000000000000002), (0.9999999999999999, 0.0)] }}} === Other improvements === Sage 9.2 has also merged a number of improvements to `sage.tensor.modules`: [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/30094|#30094]], [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/30169|#30169]], [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/30179|#30179]], [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/30181|#30181]], [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/30194|#30194]], [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/30250|#30250]], [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/30251|#30251]], [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/30254|#30254]], [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/30255|#30255]], [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/30287|#30287]] == Polyhedral geometry == === New features === It is now possible to choose which backend to use to compute regions of hyperplane arrangements [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/29506|29506]]: {{{ #!python sage: R.<sqrt5> = QuadraticField(5) sage: H = HyperplaneArrangements(R, names='xyz') sage: x,y,z = H.gens() sage: A = H(sqrt5*x+2*y+3*z, backend='normaliz') sage: A.backend() 'normaliz' sage: A.regions()[0].backend() # optional - pynormaliz 'normaliz' }}} It is now possible to compute the slack matrix of a polyhedron [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/29838|29838]]: {{{ #!python sage: P = polytopes.cube(intervals='zero_one') sage: P.slack_matrix() ⎛0 1 1 1 0 0⎞ ⎜0 0 1 1 0 1⎟ ⎜0 0 0 1 1 1⎟ ⎜0 1 0 1 1 0⎟ ⎜1 1 0 0 1 0⎟ ⎜1 1 1 0 0 0⎟ ⎜1 0 1 0 0 1⎟ ⎝1 0 0 0 1 1⎠ }}} It is now possible to apply an affine transformation on a polyhedron [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/30327|30327]]: {{{ #!python sage: M = random_matrix(QQ,3,3) sage: v = vector(QQ,(1,2,3)) sage: F = AffineGroup(3, QQ) sage: f = F(M, v); f [ 0 0 -2] [1] x |-> [ 0 1 0] x + [2] [ -1 -1 1/2] [3] sage: cube = polytopes.cube() sage: f * cube A 3-dimensional polyhedron in QQ^3 defined as the convex hull of 8 vertices sage: f(cube) # also works A 3-dimensional polyhedron in QQ^3 defined as the convex hull of 8 vertices }}} === Implementation improvements === * It is now possible to set up polyhedra with both Vrep and Hrep in the following constructions: * Linear transformation [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/29843|29843]] * Polar [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/29569|29569]] * Product [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/29583|29583]] * The generation of regions of hyperplane arrangement has been improved [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/29661|29661]] * Ehrhart related functions are now cached [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/29196|29196]] * Obtaining incidence matrix and combinatorial polyhedron is much faster for integer and rational polyhedra [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/29837|29837]], [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/29841|29841]] * The test coverage for the [[http://match.stanford.edu/reference/discrete_geometry/index.html#backends-for-polyhedra|various backends for polyhedral computations]] has been improved by using `_test_...` methods to the abstract base class `Polyhedron_base`, in addition to doctests. See [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/29842|Meta-ticket #29842 Run a more stable test suite on polyhedra]]. * The face lattice can be obtained in reasonable time and no longer leaks memory [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/28982|28982]] There are also some bug fixes and other improvements. For more details see the [[https://trac.sagemath.org/wiki/SagePolyhedralGeometry#release_9.2|release notes for optimization and polyhedral geometry software interactions in Sage]]. == Combinatorics == === Reduction from Dancing links to SAT or MILP === It is now possible to solve an instance of an [[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Exact_cover|exact cover problem]] using a reduction from a dancing links instance to SAT [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/29338|29338]] or MILP [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/29955|29955]]: {{{ #!python sage: from sage.combinat.matrices.dancing_links import dlx_solver sage: rows = [[0,1,2], [3,4,5], [0,1], [2,3,4,5], [0], [1,2,3,4,5]] sage: d = dlx_solver(rows) sage: d.one_solution() [1, 0] sage: d.one_solution_using_sat_solver('cryptominisat') [2, 3] sage: d.one_solution_using_sat_solver('glucose') [2, 3] sage: d.one_solution_using_sat_solver('glucose-syrup') [2, 3] sage: d.one_solution_using_sat_solver('picosat') [4, 5] sage: d.one_solution_using_milp_solver() [0, 1] sage: d.one_solution_using_milp_solver('Gurobi') [0, 1] }}} === Polyomino tilings === It is now possible to find a surrounding of a polyomino with copies of itself, see [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/29160|29160]]. This is based on the dancing links solver in Sage. This is motivated by the [[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Heesch%27s_problem|Heesch's problem]]. An example is below: {{{ sage: from sage.combinat.tiling import Polyomino sage: H = Polyomino([(-1, 1), (-1, 4), (-1, 7), (0, 0), (0, 1), (0, 2), ....: (0, 3), (0, 4), (0, 5), (0, 6), (0, 7), (0, 8), (1, 1), (1, 2), ....: (1, 3), (1, 4), (1, 5), (1, 6), (1, 7), (1, 8), (2, 0), (2, 2), ....: (2, 3), (2, 5), (2, 6), (2, 8)]) sage: H.show2d() }}} {{attachment:H.png}} {{{ sage: %time solution = H.self_surrounding(10, ncpus=8) CPU times: user 1.69 s, sys: 1.08 s, total: 2.77 s Wall time: 3.85 s sage: G = sum([p.show2d() for p in solution], Graphics()) sage: G }}} {{attachment:G.png}} === Fully commutative elements of Coxeter groups === It is now possible by [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/30243|30243]] to enumerate and work with the fully commutative elements of a Coxeter group. Methods to compute *star operations* and plot the *heaps* of such elements are also included. {{{ #!python sage: A3 = CoxeterGroup(['A', 3]) sage: FCA3 = A3.fully_commutative_elements() sage: FCA3.category() Category of finite enumerated sets sage: FCA3.list() [[], [1], [2], ... [1, 3, 2], [1, 2, 3], [2, 1, 3, 2]] sage: B8 = CoxeterGroup(['B', 8]) sage: FCB8 = B8.fully_commutative_elements() sage: len(FCB8) # long time (7 seconds) 14299 sage: B6 = CoxeterGroup(['B', 6]) sage: FCB6 = B6.fully_commutative_elements() sage: w = FCB6([1, 6, 2, 5, 4, 6, 5]) sage: w.coset_decomposition({5, 6}) ([6, 5, 6], [1, 2, 4, 5]) sage: w.star_operation({5,6}, 'lower') [1, 5, 2, 4, 6, 5] sage: FCB6([3, 2, 4, 3, 1]).plot_heap() }}} {{attachment:heap.png}} === BIBDs with lambda>1 === Sage can now construct a number of balanced incomplete block designs (BIBDs) with lambda>1, in particular, all the known biplanes (i.e. symmetric BIBDs with lambda=2). === Finite generalized polygons === Sage can now construct generalized quadrangles, hexagons, and octagons, and generalized quadrangles with a spread. == Graph theory == === Distance regular graphs generators === A small database of constructions for distance regular graphs is now available. 15 sporadic distance regular graphs and 8 infinite families can now be constructed. Now Sage is capable of constructing all known families of distance-regular graphs with unbounded diameter. Some code examples: {{{ #!python sage: graphs.vanLintSchrijverGraph().is_distance_regular(parameters=True) ([6, 5, 5, 4, None], [None, 1, 1, 2, 6]) sage: graphs.DoubleOddGraph(5).is_distance_regular(parameters=True) ([6, 5, 5, 4, 4, 3, 3, 2, 2, 1, 1, None], [None, 1, 1, 2, 2, 3, 3, 4, 4, 5, 5, 6]) }}} === Diameter, radius, eccentricities === State-of-the-art algorithms for computing the diameter, the radius and the eccentricities of (directed) (weighted) graphs are now available [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/29657|29657]]. {{{ #!python sage: G = graphs.RandomBarabasiAlbert(10000, 2) sage: %time G.diameter(algorithm='DHV') # now default for undirected unweighted graphs CPU times: user 74.4 ms, sys: 2.81 ms, total: 77.2 ms Wall time: 75.8 ms 9 sage: %time G.diameter(algorithm='BFS') CPU times: user 573 ms, sys: 4.04 ms, total: 577 ms Wall time: 576 ms 9 }}} === More constructions === linear codes got a function to compute its coset graph; undirected graphs got a method to quickly compute their antipodal quotients. === More iterators === Some methods have been turned to iterators to avoid returning long lists [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/23002| 23002]], [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/30470|30470]]. {{{ #!python sage: G = graphs.Grid2dGraph(3, 3) sage: cpt = 0 sage: for _ in G.spanning_trees(): ....: cpt += 1 sage: cpt 192 sage: G.spanning_trees_count() 192 sage: S = G.spanning_trees() sage: next(S) Graph on 9 vertices sage: next(S) Graph on 9 vertices }}} {{{ #!python sage: g = graphs.PathGraph(5) sage: bridges = g.bridges() sage: next(bridges) (3, 4, None) sage: next(bridges) (2, 3, None) sage: next(bridges) (1, 2, None) sage: next(bridges) (0, 1, None) sage: next(bridges) --------------------------------------------------------------------------- StopIteration Traceback (most recent call last) <ipython-input-38-cf858e1a0a30> in <module> ----> 1 next(bridges) StopIteration: }}} === Implementation improvements === * Truly linear time implementation of lex_BFS [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/11736|11736]] * Faster and memory efficient implementation for computing the distances distribution, Wiener index and Szeged index. These new implementations have linear memory consumption rather than quadratic. * We started improving the backends to speed up basic operations (edge and vertex iterations, subgraph, etc.). More to come for next release [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/28895|28895]]. == Commutative algebra == === Laurent polynomials === Rings of Laurent polynomials now support ideal creation and manipulation [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/29512|29512]]: {{{ sage: L.<x,y,z> = LaurentPolynomialRing(QQ, 3) sage: I = L.ideal([(x+y+z)^3+x*y, x^2+y^2+z^2]) sage: I.groebner_basis() (y^4 + 4*x*y*z^2 + y^2*z^2 + 2*x*z^3 + 2*y*z^3 - z^4 + 3/2*x*y*z + 1/4*x*z^2 + 1/4*y*z^2 - 1/4*z^3 + 1/8*x*y, x*y^2 - y^3 + 3*x*y*z + x*z^2 - z^3 + 1/2*x*y, x^2 + y^2 + z^2) sage: (x^3+y^3+z^3) in I False sage: x + x^-1*y^2 + x^-1*z^2 in I True }}} === Motivic multiple zetas === The ring of motivic multiple zeta values has been implemented, using algorithms of Francis Brown. It allows to compute at least up to weight 12 [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/22713|22713]]. {{{ sage: Multizeta(1,2)**2 12*ζ(1,1,1,3) + 6*ζ(1,1,2,2) + 2*ζ(1,2,1,2) sage: Multizeta(1,2)==Multizeta(3) True sage: Multizeta(2,3,4).n(100) 0.0029375850405618494701189454256 }}} The numerical evaluation is based on PARI implementation. === Power series === There is a new method to compute the coefficients in the Jacobi continued fraction expansion of a power series [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/29789|29789]]. {{{ sage: t = QQ[['t']].0 sage: f = sum(factorial(n)*t**n for n in range(20)).O(20) sage: f.jacobi_continued_fraction() ((-1, -1), (-3, -4), (-5, -9), (-7, -16), (-9, -25), (-11, -36), (-13, -49), (-15, -64), (-17, -81)) }}} === Ring homomorphisms === For many polynomial ring homomorphisms, the methods `inverse`, `is_invertible`, `is_injective`, `is_surjective`, `kernel` and `inverse_image` have been implemented. This covers not only polynomial rings, but also quotient rings, number fields and Galois fields. [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/9792|#9792]] [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/29723|#29723]] {{{ sage: R.<x,y,z> = QQ[] sage: sigma = R.hom([x - 2*y*(z*x+y^2) - z*(z*x+y^2)^2, y + z*(z*x+y^2), z], R) sage: tau = sigma.inverse(); tau Ring endomorphism of Multivariate Polynomial Ring in x, y, z over Rational Field Defn: x |--> -y^4*z - 2*x*y^2*z^2 - x^2*z^3 + 2*y^3 + 2*x*y*z + x y |--> -y^2*z - x*z^2 + y z |--> z sage: (tau * sigma).is_identity() True }}} The method `inverse_image` can be used to test whether an element is contained in a subalgebra: {{{ sage: R.<s,t> = PolynomialRing(QQ) sage: S.<x,y,z,w> = PolynomialRing(QQ) sage: f = S.hom([s^4, s^3*t, s*t^3, t^4], R) sage: f.inverse_image(R.ideal(0)) Ideal (y*z - x*w, z^3 - y*w^2, x*z^2 - y^2*w, y^3 - x^2*z) of Multivariate Polynomial Ring in x, y, z, w over Rational Field sage: f.inverse_image(s^3*t^4*(s+t)) x*w + y*w sage: f.inverse_image(s^2*t^2) ... ValueError: element s^2*t^2 does not have preimage }}} == Manifolds == === diff function for exterior derivatives === It is now possible to invoke '''diff''' to compute the differential (exterior derivative) of a differentiable form ([[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/29953|#29953]]). For instance, for a scalar field: {{{ sage: M = Manifold(2, 'M') sage: X.<x,y> = M.chart() sage: f = M.scalar_field(x^2*y, name='f') sage: diff(f) 1-form df on the 2-dimensional differentiable manifold M sage: diff(f).display() df = 2*x*y dx + x^2 dy }}} and for a 1-form: {{{ sage: a = M.one_form(-y, x, name='a'); a.display() a = -y dx + x dy sage: diff(a) 2-form da on the 2-dimensional differentiable manifold M sage: diff(a).display() da = 2 dx/\dy }}} === Dot and cross products of vector fields along a curve === The methods '''dot_product()''', '''cross_product()''' and '''norm()''' can be now be used for vector fields defined along a differentiable map, the codomain of which is a Riemannian manifold ([[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/30318|#30318]]). Previously, these methods worked only for vector fields ''on'' a Riemannian manifold, i.e. along the identity map. An important subcase is of course that of a curve in a Riemannian manifold. For instance, let us consider a helix ''C'' in the Euclidean space E^3^ parametrized by its arc length ''s'': {{{ sage: E.<x,y,z> = EuclideanSpace() sage: R.<s> = RealLine() sage: C = E.curve((2*cos(s/3), 2*sin(s/3), sqrt(5)*s/3), (s, -oo, +oo), ....: name='C') sage: C.display() C: R --> E^3 s |--> (x, y, z) = (2*cos(1/3*s), 2*sin(1/3*s), 1/3*sqrt(5)*s) }}} The tangent vector field ''T=C' '' has a unit norm since the parameter ''s'' is the arc length: {{{ sage: T = C.tangent_vector_field() sage: T.display() C' = -2/3*sin(1/3*s) e_x + 2/3*cos(1/3*s) e_y + 1/3*sqrt(5) e_z sage: norm(T) Scalar field |C'| on the Real interval (0, 6*pi) sage: norm(T).expr() 1 }}} We introduce the unit normal vector ''N'' via the derivative of ''T'': {{{ sage: T_prime = R.vector_field([diff(T[i], s) for i in E.irange()], dest_map=C, ....: name="T'") sage: N = T_prime / norm(T_prime) sage: N.display() -cos(1/3*s) e_x - sin(1/3*s) e_y }}} and we get the binormal vector ''B'' as the cross product of ''T'' and ''N'': {{{ sage: B = T.cross_product(N) sage: B Vector field along the Real number line R with values on the Euclidean space E^3 sage: B.display() 1/3*sqrt(5)*sin(1/3*s) e_x - 1/3*sqrt(5)*cos(1/3*s) e_y + 2/3 e_z }}} We can then form the '''Frenet-Serret''' frame: {{{ sage: FS = R.vector_frame(('T', 'N', 'B'), (T, N, B), ....: symbol_dual=('t', 'n', 'b')) sage: FS Vector frame (R, (T,N,B)) with values on the Euclidean space E^3 }}} and check that it is orthonormal: {{{ sage: matrix([[u.dot(v).expr() for v in FS] for u in FS]) [1 0 0] [0 1 0] [0 0 1] }}} The Frenet-Serret formulas, expressing the '''curvature''' and '''torsion''' of ''C'', are obtained as: {{{ sage: N_prime = R.vector_field([diff(N[i], s) for i in E.irange()], ....: dest_map=C, name="N'") sage: B_prime = R.vector_field([diff(B[i], s) for i in E.irange()], ....: dest_map=C, name="B'") sage: for v in (T_prime, N_prime, B_prime): ....: v.display(FS) ....: T' = 2/9 N N' = -2/9 T + 1/9*sqrt(5) B B' = -1/9*sqrt(5) N }}} === Orientability of manifolds and vector bundles === It is now possible to define an orientation [[https://doc.sagemath.org/html/en/reference/manifolds/sage/manifolds/differentiable/manifold.html#sage.manifolds.differentiable.manifold.DifferentiableManifold.orientation|on a differentiable manifold]] and [[https://doc.sagemath.org/html/en/reference/manifolds/sage/manifolds/vector_bundle.html#sage.manifolds.vector_bundle.TopologicalVectorBundle.orientation|on a vector bundle]] ([[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/30178|#30178]]). [[https://doc.sagemath.org/html/en/reference/manifolds/sage/manifolds/manifold.html#sage.manifolds.manifold.TopologicalManifold.orientation|Orientations of topological manifolds]] have also been introduced, according to [[http://www.map.mpim-bonn.mpg.de/Orientation_of_manifolds|this definition]]. === Euclidean spaces as metric spaces === Euclidean spaces have been endowed with a distance function and have been set in the category of complete metric spaces ([[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/30062|#30062]]): {{{ sage: E.<x,y> = EuclideanSpace() sage: p = E((1,0)) # the point of coordinates (1,0) sage: q = E((0,2)) # the point of coordinates (0,2) sage: d = E.dist # the distance function sage: d(p,q) sqrt(5) sage: p.dist(q) sqrt(5) sage: E.category() Join of Category of smooth manifolds over Real Field with 53 bits of precision and Category of complete metric spaces }}} === Bundle connections === Bundle connections have been improved ([[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/30208|#30208]]) and their action on vector fields and sections has been implemented ([[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/30209|#30209]]). === Internal code improvements and bug fixes === Many improvements/refactoring of the code have been performed in this release: * [[https://doc.sagemath.org/html/en/reference/manifolds/manifold.html|topological part]]: [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/30266|#30266]], [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/30267|#30267]], [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/30291|#30291]]. * [[https://doc.sagemath.org/html/en/reference/manifolds/diff_manifold.html|differentiable part]]: [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/30228|#30228]], [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/30274|#30274]], [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/30280|#30280]], [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/30285|#30285]], [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/30288|#30288]], [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/30538|#30538]]. In addition, various bugs have been fixed: [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/30108|#30108]], [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/30112|#30112]], [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/30191|#30191]], [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/30275|#30275]], [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/30289|#30289]], [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/30320|#30320]], [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/30401|#30401]], [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/30519|#30519]]. == Algebra == === Lie Conformal Algebras === Implemented Lie conformal algebras and superalgebras. Here are some examples of their usage: {{{ sage: V = lie_conformal_algebras.Virasoro(QQ); V The Virasoro Lie conformal algebra over Rational Field sage: V.inject_variables() Defining L, C sage: L.bracket(L) {0: TL, 1: 2*L, 3: 1/2*C} sage: L.T(2).bracket(L) {2: 2*TL, 3: 12*L, 5: 10*C} sage: V = lie_conformal_algebras.NeveuSchwarz(QQ) sage: V.some_elements() [L, G, C, TG, TG + 4*T^(2)G, 4*T^(2)G] sage: W = lie_conformal_algebras.FreeFermions(QQbar, 2); W The free Fermions super Lie conformal algebra with generators (psi_0, psi_1, K) over Algebraic Field sage: W.inject_variables() Defining psi_0, psi_1, K sage: psi_0.bracket(psi_1.T()) {} sage: psi_0.bracket(psi_0.T()) {1: K} sage: psi_0.is_even_odd() 1 }}} For documentation on implemented features see [[https://doc.sagemath.org/html/en/reference/algebras/sage/algebras/lie_conformal_algebras/lie_conformal_algebra.html|Lie Conformal Algebra]]. For a list of implemented examples see [[https://doc.sagemath.org/html/en/reference/algebras/sage/algebras/lie_conformal_algebras/examples.html|Lie Conformal Algebra Examples]]. === Differential Weyl algebra === The action of differential operators from the Weyl algebra on polynomials has been implemented [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/29928|#29928]]: {{{ sage: W.<x,y> = DifferentialWeylAlgebra(QQ) sage: dx, dy = W.differentials() sage: dx.diff(x^3) 3*x^2 sage: (x*dx + dy + 1).diff(x^4*y^4 + 1) 5*x^4*y^4 + 4*x^4*y^3 + 1 }}} == Improved Unicode support == === Unicode identifiers === Python 3 made much improved support for Unicode available, and Sage 9.2 has merged several Unicode improvements. Note that Python does not allow ''arbitrary'' Unicode characters in identifiers but only [[https://docs.python.org/3/reference/lexical_analysis.html#identifiers|word constituents]]. So before you get excited about using emojis... note that they cannot be used: {{{ #!python sage: K.<🍎,🥝> = QQ[] SyntaxError: invalid character in identifier }}} However, we can use letters from various alphabets. The updated IPython allows us to type them using [[https://ipython.readthedocs.io/en/stable/api/generated/IPython.core.completer.html|latex and unicode tab completion]]: {{{ #!python sage: μ, ν, ξ = 1, 2, 3 # type \mu<TAB>, # \nu<TAB>, ... sage: SR('λ + 2λ') 3*λ sage: var('α', domain='real') α sage: Ш = EllipticCurve('389a').sha() # type \CYR<TAB> CAP<TAB> # LET<TAB> SHA<TAB><ENTER> sage: Ш Tate-Shafarevich group for the Elliptic Curve defined by y^2 + y = x^3 + x^2 - 2*x over Rational Field sage: GelʹfandT͡setlinPattern = GelfandTsetlinPattern # type \MODIFIER LETTER # PRIME<TAB><ENTER> # for the romanized soft mark sage: ГельфандЦетлинPattern = GelʹfandT͡setlinPattern sage: ГельфандЦетлинPattern([[3, 2, 1], [2, 1], [1]]).pp() 3 2 1 2 1 1 sage: 四次方(x) = x^4 sage: 四次方(3) 81 }}} We can use math accents... {{{ #!python sage: a = 1 sage: â = 2 # type a\hat<TAB><ENTER> sage: ā = 3 # type a\bar<TAB><ENTER> sage: a, â, ā (1, 2, 3) sage: s(t) = t^3; s t |--> t^3 sage: ṡ = diff(s, t); ṡ # type s\dot<TAB><ENTER> t |--> 3*t^2 sage: s̈ = diff(ṡ, t); s̈ # type s\ddot<TAB><ENTER> t |--> 6*t }}} ... and have fun with modifier letters: {{{ #!python sage: ℚ̄ = QQbar # type \bbQ<TAB>\bar<TAB> sage: %display unicode_art sage: A = matrix(ℚ̄, [[1, 2*I], [3*I, 4]]); A ⎛ 1 2*I⎞ ⎝3*I 4⎠ sage: Aᵀ = A.transpose() # type A\^T<TAB><ENTER> sage: Aᵀ ⎛ 1 3*I⎞ ⎝2*I 4⎠ sage: Aᴴ = A.conjugate_transpose() # type A\^H<TAB><ENTER> sage: Aᴴ ⎛ 1 -3*I⎞ ⎝-2*I 4⎠ sage: C = Cone([[1, 1], [0, 1]]) sage: Cᵒ = C.dual(); Cᵒ # type C\^o<TAB><ENTER> 2-d cone in 2-d lattice M }}} But note that Python [[https://stackoverflow.com/questions/34097193/identifier-normalization-why-is-the-micro-sign-converted-into-the-greek-letter|normalizes identifiers]], so the following variants are ''not'' distinguished: {{{ #!python sage: AT == Aᵀ, AH == Aᴴ, Co == Cᵒ (True, True, True) sage: ℚ = QQ # type \bbQ<TAB><ENTER> sage: ℚ Rational Field sage: Q = 42 sage: ℚ 42 sage: F = 1 sage: 𝐹, 𝐅, 𝓕, 𝕱, 𝗙, 𝘍, 𝙁, 𝙵 # type \itF<TAB>, \bfF<TAB>, # \scrF<TAB>, \frakF<TAB>, # \sansF<TAB>, ... (1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1) }}} We have also added a few Unicode aliases for global constants and functions. {{{ #!python sage: π pi sage: _.n() 3.14159265358979 sage: Γ(5/2) 3/4*sqrt(pi) sage: ζ(-1) -1/12 }}} See [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/30111|Meta-ticket #30111: Unicode support]] for more information. === Unicode characters allowed in tensor index notation === Greek letters (and more generally any Unicode non-digit word-constituent character) are now allowed in index notation for tensors ([[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/29248|#29248]]). For instance, taking the trace of a type-(1,1) tensor field: {{{ sage: E.<x,y> = EuclideanSpace() sage: t = E.tensor_field(1, 1, [[x, 1], [0, y]]) sage: t['^μ_μ'] Scalar field on the Euclidean plane E^2 sage: t['^μ_μ'] == t.trace() True }}} === Unicode art === * [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/30119|#30119]] Implemented a general function for writing integers as unicode sub/superscripts. * In [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/29205|#29205]], some Lie algebra elements now have better unicode support: {{{ sage: L = LieAlgebra(QQ, cartan_type="A2", representation='matrix') sage: unicode_art(L.an_element()) ⎛ 1 1 0⎞ ⎜ 1 0 1⎟ ⎝ 0 1 -1⎠ sage: L = lie_algebras.Heisenberg(QQ, 2) sage: unicode_art(sum(L.basis())) p₁ + p₂ + q₁ + q₂ + z sage: L = lie_algebras.VirasoroAlgebra(QQ) sage: unicode_art(L.an_element()) d₋₁ + d₀ - 1/2 + c sage: L = LieAlgebra(QQ, cartan_type=['A',1,1]) sage: unicode_art(L.an_element()) ( alpha[1] + alphacheck[1] + -alpha[1] )⊗t⁰ + ( -alpha[1] )⊗t¹ + ( alpha[1] )⊗t⁻¹ + c + d sage: L.<x,y> = LieAlgebra(QQ) sage: unicode_art(x.bracket(y)) [x, y] sage: L = LieAlgebra(QQ, cartan_type=['A',2], representation="compact real") sage: unicode_art(L.an_element()) ⎛ i i + 1 i + 1⎞ ⎜i - 1 i i + 1⎟ ⎝i - 1 i - 1 -2*i⎠ }}} * As part of [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/29696|#29696]], Temperley-Lieb diagrams now have unicode (and ascii) art: {{{ sage: from sage.combinat.diagram_algebras import TL_diagram_ascii_art sage: TL = [(-15,-12), (-14,-13), (-11,15), (-10,14), (-9,-6), ....: (-8,-7), (-5,-4), (-3,1), (-2,-1), (2,3), (4,5), ....: (6,11), (7, 8), (9,10), (12,13)] sage: TL_diagram_ascii_art(TL, use_unicode=False) o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o | `-` `-` | `-` `-` | `-` | | | `---------` | | | .-------` | `---. | .-------` | .-----. | | .-----. .-. | .-. | .-. | | | | .-. | o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o sage: TL_diagram_ascii_art(TL, use_unicode=True) ⚬ ⚬ ⚬ ⚬ ⚬ ⚬ ⚬ ⚬ ⚬ ⚬ ⚬ ⚬ ⚬ ⚬ ⚬ │ ╰─╯ ╰─╯ │ ╰─╯ ╰─╯ │ ╰─╯ │ │ │ ╰─────────╯ │ │ │ ╭───────╯ │ ╰───╮ │ ╭───────╯ │ ╭─────╮ │ │ ╭─────╮ ╭─╮ │ ╭─╮ │ ╭─╮ │ │ │ │ ╭─╮ │ ⚬ ⚬ ⚬ ⚬ ⚬ ⚬ ⚬ ⚬ ⚬ ⚬ ⚬ ⚬ ⚬ ⚬ ⚬ }}} |
| Line 19: | Line 972: |
| * [[https://groups.google.com/d/msg/sage-devel/9gOkmF6rSjY/wEV4WBQABwAJ|sage-devel: require "./configure" before "make"]], [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/29316|Trac #29316]] == Tickets == * [[https://trac.sagemath.org/query?status=needs_info&status=needs_review&status=needs_work&status=new&summary=~Meta&col=id&col=summary&col=status&col=type&col=priority&col=milestone&col=component&order=priority|Open Meta-Tickets]] |
=== Initial configuration with ./configure required === Sage 9.1 introduced [[https://wiki.sagemath.org/ReleaseTours/sage-9.1#Portability_improvements.2C_increased_use_of_system_packages|informational messages at the end of a ./configure run]] regarding system packages. To make sure that these messages are not overlooked, Sage 9.2 no longer invokes `./configure` when you type `make` in an unconfigured source tree. See [[https://groups.google.com/d/msg/sage-devel/9gOkmF6rSjY/wEV4WBQABwAJ|sage-devel: require "./configure" before "make"]], [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/29316|#29316]]. === Support for gcc/gfortran 10.x added === All standard Sage packages have been upgraded in Sage 9.2 so that they build correctly using gcc/gfortran 10.x. The Sage `./configure` script therefore now accepts these compiler versions. === Selecting a system Python to use for Sage's venv === The `configure` script in Sage 9.2 has been changed so it only looks for a binary named `python3` in your `PATH`. If Sage cannot find a suitable `python3` in your `PATH`, it will build its own copy of Python 3.8.5. Sage no longer looks for versioned Python binaries such as `python3.7`, [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/30546|#30546]]. To configure Sage to use a specific Python installation, you can use `./configure --with-python=/path/to/python3`. The `configure` script will test whether this installation is suitable for Sage and will exit with an error otherwise. === System package information for more distributions === System package information has been added for [[https://www.gentoo.org/|Gentoo Linux]], [[https://www.freebsd.org/|FreeBSD]], [[https://voidlinux.org/|Void Linux]], and [[https://nixos.org/|NixOS]]. === System package information for optional packages at runtime === When a user tries to use a feature depending on an optional package is not installed, Sage now issues advice regarding the packages that should be installed to provide the feature -- using either the system package manager, `pip`, or (in the Sage distribution) `sage -i` [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/30606|#30606]]. (For packagers: For this to work, either `SAGE_ROOT/build/pkgs/*/distros/` and `SAGE_ROOT/build/bin/{sage-get-system-packages, sage-guess-package-system, sage-print-system-package-command}` need to be installed, or alternative implementations of these scripts need to be provided.) === For developers: Changes to the build system of sagelib === Let's talk about `setup.py`. The build system of the Sage library, in `build/pkgs/sagelib/src/setup.py`, is based on `distutils` (not `setuptools`); it is implemented in the package `sage_setup`. In particular, it implements its own version of source code discovery methods similar to [[https://setuptools.readthedocs.io/en/latest/setuptools.html#using-find-packages|setuptools.find_packages]]: `sage_setup.find.find_python_sources`. Because of source discovery, developers can add new Python modules and packages under `src/sage/` simply by creating files and directories; it is not necessary to edit `setup.py`. Prior to Sage 9.2, the situation was different for Cython extensions. They had to be listed in `src/module_list.py`, either one by one, or using glob patterns such as `*` and `**`. Sage 9.2 has eliminated the need for `src/module_list.py` by extending `sage_setup.find.find_python_sources`; it now also finds Cython modules in the source tree (Trac [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/29701|#29701]]). Some Cython modules need specific compiler and linker flags. Sage 9.2 has moved all of these flags from `Extension` options in `src/module_list.py` to `distutils:` directives in the individual `.pyx` source files, see [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/29706|#29706]] and [[https://cython.readthedocs.io/en/latest/src/userguide/source_files_and_compilation.html#compiler-directives|Cython documentation]]. Sage 9.2 has also changed the mechanism for conditionalizing a Cython extension module on the presence of a Sage package. Consider the module [[https://git.sagemath.org/sage.git/tree/src/sage/graphs/graph_decompositions/tdlib.pyx?id=55c3fbc565fd7884f3df9555de83dd326ace276e|sage.graphs.graph_decompositions.tdlib]] as an example. Prior to Sage 9.2, this module was declared as an `OptionalExtension`, conditional on the SPKG `tdlib`, in `src/module_list.py`. The new mechanism is as follows. [[https://git.sagemath.org/sage.git/tree/src/setup.py?id=55c3fbc565fd7884f3df9555de83dd326ace276e#n53|src/setup.py]] maps the SPKG name `tdlib` to the "distribution name" `sage-tdlib`. At the top of the Cython source file [[https://git.sagemath.org/sage.git/tree/src/sage/graphs/graph_decompositions/tdlib.pyx?id=55c3fbc565fd7884f3df9555de83dd326ace276e|src/sage/graphs/graph_decompositions/tdlib.pyx]], there is a new directive `sage_setup: distribution = sage-tdlib`. Now the source discovery in [[https://git.sagemath.org/sage.git/tree/src/sage_setup/find.py?id=55c3fbc565fd7884f3df9555de83dd326ace276e#n61|sage_setup.find.find_python_sources]] includes this Cython module only if the SPKG `tdlib` is installed and current. == New development tools == === Testing and linting with tox === [[https://tox.readthedocs.io/en/latest/|tox]] is a popular package that is used by a large number of Python projects as the standard entry point for testing and linting. Sage 9.1 started to use tox for [[https://doc.sagemath.org/html/en/developer/portability_testing.html#automatic-docker-based-build-testing-using-tox|portability testing of the Sage distribution]], which requires an installation of tox in the system python. Sage 9.2 has added a tox configuration (`src/tox.ini`) for the (more typical) use of tox for testing and linting of the Sage library [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/30453|#30453]]. This provides an entry point for various testing/linting methods that is more idiomatic from the viewpoint of the Python community. The commands `sage -t`, `sage -coverage`, `sage -coverageall`, and `sage -startuptime` are repackaged as `sage --tox`, as the following output from `sage -advanced` indicates: {{{ $ ./sage -advanced SageMath version 9.2 ... Testing files: ... --tox [options] <files|dirs> -- general entry point for testing and linting of the Sage library -e <envlist> -- run specific test environments (default: run all) doctest -- run the Sage doctester (same as "sage -t") coverage -- information about doctest coverage of files (same as "sage --coverage[all]") startuptime -- display how long each component of Sage takes to start up (same as "sage --startuptime") }}} Three new linting methods are added: {{{ pycodestyle -- check against the Python style conventions of PEP8 relint -- check whether some forbidden patterns appear (includes all patchbot pattern-exclusion plugins) codespell -- check for misspelled words in source code }}} This functionality is available after installing the optional `tox` package using `sage -i tox` (or having tox available in the system). === Reusable wheels for the Python packages built by the Sage distribution === Sage 9.2 has changed the build process of all Python packages in the Sage distribution so that [[https://realpython.com/python-wheels/|wheels]] are built and stored in `$SAGE_LOCAL/var/lib/sage/wheels/` [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/29500|#29500]]. Users can install these wheels into virtual environments that use the same base python version, using standard tools such as `pip install --find-links`. Example: {{{ $ local/bin/python3 -m venv some-venv $ cd some-venv/ $ bin/pip3 install -v --no-index --find-links=../local/var/lib/sage/wheels/ Pillow }}} The installation is very fast because it does not involve compilation. Note: Many of these wheels include extension modules that refer to libraries in the Sage installation in `$SAGE_LOCAL` with hard-coded paths. Therefore the wheels are [[https://realpython.com/python-wheels/#bundling-shared-libraries|not immediately]] suitable for distribution. == Cleaning == * [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/29636|#29636: Delete changelog sections from all SPKG information files]]; they were deprecated in favor of using Trac years ago. The contributions of Sage developers maintaining SPKGs are documented by our [[http://www.sagemath.org/changelogs/index.html|historical changelogs]]. * Removing support for Python 2 allowed us to remove several backport packages in [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/29754|#29754]] * We also removed the deprecated SageNB (superseded a long time ago by the Jupyter notebook) in [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/29754|#29754]] and several of its dependencies. For converting old Sage worksheet files (*.sws), the script `sage -sws2rst` is available. (In Sage 9.0 and 9.1, it was available only in Python 2 builds of Sage; in [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/28838|#28838]], it was ported to Python 3.) * Support for installing "old-style Sage packages" (`.spkg` files), [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/19158|deprecated in Sage 6.9]], has been removed in [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/29289|#29289]], after making the last two missing packages, `cunningham_tables` and `polytopes_db_4d`, available as normal optional Sage packages. Users who wish to package their own Sage code for distribution may find a [[https://wiki.sagemath.org/SageMathExternalPackages|list of external packages]] helpful, many of which follow best practices in packaging. * The use of `sage.misc.package` has been essentially eliminated from the Sage library by transitioning to `sage.feature`; see [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/30607|#30607]], [[https://trac.sagemath.org/ticket/30616|#30616]]. == Availability of Sage 9.2 and installation help == !SageMath 9.2 was released on 2020-10-24; it is available in the [[https://github.com/sagemath/sage/tree/9.1|sage git repository]], and the self-contained [[http://www.sagemath.org/download-source.html|source tarballs are available]] for download. Sage 9.2 has been [[https://github.com/sagemath/sage/actions/runs/326227813|tested to compile from source on a wide variety of platforms]], including: * Linux 64-bit (x86_64) * ubuntu-{trusty,xenial,bionic,eoan,focal,groovy}, * debian-{jessie,stretch,buster,bullseye,sid}, * linuxmint-{17,18,19,19.3}, * fedora-{26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33}, * centos-{7,8}, * archlinux, * slackware-14.2, * conda-forge * Linux 32-bit (i386) * debian-buster * ubuntu-eoan * macOS * macOS Catalina and older (macOS 10.x, with Xcode 11.x or Xcode 12) * optionally, using Homebrew * optionally, using conda-forge * note that macOS 11 beta ("Big Sur") is ''not'' supported * Windows (Cygwin-64). === Binaries === * TBA === Availability in distributions === See [[https://repology.org/project/sagemath/versions|repology.org: sagemath]] === Installation FAQ === See [[https://github.com/sagemath/sage/blob/9.2/README.md|README.md]] in the source distribution for installation instructions. See [[https://groups.google.com/forum/#!forum/sage-release|sage-release]], [[https://groups.google.com/forum/#!forum/sage-devel|sage-devel]]. == More details == * [[https://www.sagemath.org/changelogs/sage-9.2.txt|Sage 9.2 changelog]] |
| Line 26: | Line 1123: |
== Availability of Sage 9.2 and installation help == The Sage 9.2 series has not been started yet. * See [[https://groups.google.com/forum/#!forum/sage-devel|sage-devel]] for development discussions. |
Sage 9.2 Release Tour
released October 24, 2020
Contents
-
Sage 9.2 Release Tour
- Python 3 transition completed
- Package upgrades
- Graphics
- Linear and multilinear algebra
- Polyhedral geometry
- Combinatorics
- Graph theory
- Commutative algebra
- Manifolds
- Algebra
- Improved Unicode support
- Configuration and build changes
- New development tools
- Cleaning
- Availability of Sage 9.2 and installation help
- More details
Python 3 transition completed
SageMath 9.0 was the first version of Sage running on Python 3 by default. SageMath 9.1 continued to support Python 2.
Support for Python 2 removed
Sage 9.2 has removed support for Python 2. The Sage library now makes use of Python language and library features that are only available in Python 3.6 or newer; and large amounts of compatibility code have been removed.
However, note that this is unrelated to the minimal requirements for a source installation of the Sage distribution: Sage 9.2 is still able to build on a system that only provides Python 2.x or Python 3.5 or older. In this case, the SageMath distribution builds its own copy of Python 3.
Support for Python 3.6, 3.8, and 3.9 added
Sage 9.2 has added support for Python 3.8 in #27754 and Python 3.9 in #30184.
Sage 9.2 has also added support for Python 3.6. This allows Sage to use the system Python on some older Linux distributions that are still in widespread use in scientific computing, including centos-8 and fedora-{26,27,28} (although Python 3.7.x packages are also available for these). See #29033 for more details.
Hence, Sage 9.2 conforms to (and exceeds) NumPy Enhancement Proposal 29 regarding Python version support policies.
If no suitable system Python, versions 3.6.x, 3.7.x, 3.8.x, or 3.9.x is found, Sage installs its own copy of Python 3 from source. The version of Python shipped with the Sage distribution has been upgraded from 3.7.3 to 3.8.5.
For developers: Using Python 3.6+ features in sagelib
Meta-ticket #29756 provides a starting point for a discussion of new features of the Python language and standard library to bring them to systematic use in sagelib. All features provided by Python 3.6 can be used immediately; features introduced in Python 3.7 or later will require backporting or a decision to drop the goal of supporting Python 3.6.
More details
Trac tickets with keyword/component python3 in milestone 9.2
See Python3-Switch for more details.
Package upgrades
The removal of support for Python 2 has enabled major package upgrades.
Major user-visible package upgrades below...
matplotlib
Dropping Python 2 support allowed us to make a major jump from matplotlib 2.2.5 to 3.3.1. See matplotlib's release notes for 3.0, 3.1, 3.2,3.3. In addition to improved output, this update will likely enable Sage developers to implement new features for plotting and graphics.
rpy2 and R
The rpy2 Python package is the foundation for SageMath's interface to R. Dropping Python 2 support allowed us to make the major upgrade from 2.8.2 to 3.3.5 in #29441; see the release notes for details.
We only did a minor upgrade of R itself in the Sage distribution, to 3.6.3, the latest in the 3.6.x series. Of course, if R 4.0.x is installed in the system, Sage will use it instead of building its own copy.
The SageMath developers are eager to learn from users how they use the SageMath-R interface, and what needs to be added to it to become more powerful. Let us know at sage-devel.
sphinx
Sage uses Sphinx to build its documentation. Sage 9.2 has updated Sphinx from 1.8.5 to 3.1.2; see Sphinx release notes for more information.
SymPy
SymPy has been updated from 1.5 to 1.6.2 in #29730, #30425. See the Release notes.
IPython, Jupyter notebook, JupyterLab
Dropping support for Python 2 allowed us to upgrade IPython from 5.8.0 to 7.13.0 in #28197. See the release notes for the 6.x and 7.x series.
We have also upgraded the Jupyter notebook from 5.7.6 to 6.1.1 in #26919; see the notebook changelog for more information. Besides, the pdf export of Jupyter notebooks has been fixed, so that LaTeX-typeset outputs are now rendered in the pdf file (#23330).
JupyterLab is now fully supported as an optional, alternative interface #30246, including interacts. To use it, install it first, using the command sage -i jupyterlab_widgets. Then you can start it using ./sage -n jupyterlab.
Normaliz
The optional package Normaliz, a tool for computations in affine monoids, vector configurations, lattice polytopes, rational cones, and algebraic polyhedra has been upgraded from 3.7.2 to 3.8.8, and PyNormaliz to version 2.12.
The upgrade adds support for incremental ("dynamic") computations, the computation of automorphism groups and refined triangulations of cones and polyhedra, and limited support for semiopen cones and polyhedra.
To install Normaliz and PyNormaliz, use sage -i pynormaliz.
SageTeX
Updated to version 3.5, improving Python 3 compatibility, also updated to version 3.5 on CTAN.
Other package updates
For developers: Upgrading packages
Upgrading Python packages in the Sage distribution from PyPI has again become easier, thanks to #20104. You can now do:
$ sage --package update-latest matplotlib Updating matplotlib: 3.3.0 -> 3.3.1 Downloading tarball to ...matplotlib-3.3.1.tar.bz2 [...............................................................]
When you do this, please remember to check that the checksums.ini file has an upstream_url in the format upstream_url=https://pypi.io/packages/source/m/matplotlib/matplotlib-VERSION.tar.gz. (This is not needed for updated-latest to work, but helps with automated tests of the upgrade ticket -- see Sage 9.1 release tour on this topic.)
For packagers: Changes to packages
The packages giacpy_sage and sage_brial have been merged into sagelib as sage.libs.giac and sage.rings.polynomial.pbori.
The directory build/pkgs/sage_sws2rst/src contains a new pip-installable package, providing the script sage-sws2rst.
The Sage library is now built out of the directory build/pkgs/sagelib/src/. A pip-installable source distribution (sdist) can be built using the script build/pkgs/sagelib/spkg-src (#29411, #29950).
The scripts in src/bin/ are now installed by sagelib's setup.py (#21559). Also several scripts have been moved to build/bin/, and some obsolete scripts have been removed (#29825, #27171).
Many build-related functions of the main Sage script, src/bin/sage (installed as sage), have been moved to a script build/bin/sage-site (not installed) in #29111. It is hoped that downstream distribution packaging is able to use this cleaned up script instead of replacing it with an ad-hoc distribution-specific script -- so that users can rely on a consistent interface. Contributions of further clean ups and refactoring of the script are welcome.
Graphics
New features
Specify the rectangle in which to draw a matrix using the new xrange and yrange options of matrix_plot. For example, to draw a matrix in [0,1]×[0,1] instead of the default [-0.5,4.5]×[-0.5,4.5]: matrix_plot(identity_matrix(5), xrange=(0, 1), yrange=(0, 1)). 27895 (Markus Wageringel)
Set the initial camera orientation in Three.js plots using the new viewpoint option. Pass it a list/tuple of the form [[x,y,z],angle], such as that provided by the existing Get Viewpoint option accessible from the menu button in the lower-right corner of a Three.js plot. 29192 (Paul Masson)
- Change the size, font, and opacity of text displayed in the Three.js viewer. For example:
30614 (Joshua Campbell)
Save a 3D graphics object directly to an HTML file that uses the Three.js viewer, similar to how you would save a PNG image: G.save('plot.html'). 29194 (Joshua Campbell)
Produce an interactive 3D animation that you can pan, rotate, and zoom while the animation is playing using the Three.js viewer. A slider and buttons for controlling playback are included on the page by default. To use this new feature construct an animation as you normally would, passing a list of still frames to the animate function, then call the interactive method. For example:
1 def build_frame(t): 2 """Build a single frame of animation at time t.""" 3 e = parametric_plot3d([sin(x-t), 0, x], 4 (x, 0, 2*pi), color='red') 5 b = parametric_plot3d([0, -sin(x-t), x], 6 (x, 0, 2*pi), color='green') 7 return e + b 8 9 frames = [build_frame(t) 10 for t in (0, pi/32, pi/16, .., 2*pi)] 11 animate(frames, delay=5).interactive( 12 projection='orthographic')
29194 (Joshua Campbell)
Implementation improvements
Points are now sampled exponentially when scale='semilogx' or scale='loglog' is specified. This decreases the number of points necessary for an accurate plot (and also increases the chance that the default number of points will produce an acceptable plot). 29523 (Blair Mason)
Points and lines are now ignored in STL 3D export. Moreover disjoint union of surfaces can be saved. 29732 (Frédéric Chapoton)
Three.js has been upgraded to version r117. 29809 (Paul Masson)
Long text is no longer clipped in Three.js plots. Multi-line text is not yet supported but is in the works. 29758 (Joshua Campbell)
JSmol's telemetry functionality has been disabled. It will no longer phone home when, for example, using viewer='jmol' in a Jupyter notebook. 30030 (Joshua Campbell)
- SVG export has been added to the javascript graph display tool:
G.show(method='js') 29807
For developers
Clarified that example Three.js plots in the documentation should use the online=True viewing option. 30136 (Paul Masson)
Linear and multilinear algebra
One free module constructor to rule them all
Sage has several specialized implementation classes for free modules and vector spaces. The factory functions FreeModule and VectorSpace select the appropriate class depending on the base ring and other parameters:
The free modules (vector spaces) created here have a distinguished standard basis indexed by range(rank).
In Sage 9.2, these factory functions have been extended in #30194 so that they cover two more cases:
1. If a sequence or family of indices is passed instead of the rank (dimension), then a CombinatorialFreeModule is created instead. These modules underly SageMath's facilities for algebraic combinatorics.
1 sage: U = FreeModule(AA, ['x', 'y', 'z']); U
2 Free module generated by {'x', 'y', 'z'} over Algebraic Real Field
3 sage: V = VectorSpace(QQ, ZZ); V
4 sage: V.basis()
5 Lazy family
6 (Term map from Integer Ring
7 to Free module generated by Integer Ring over Rational Field(i))
8 _{i in Integer Ring}
9 sage: QQ^SymmetricGroup(4)
10 Free module generated by
11 Symmetric group of order 4! as a permutation group over Rational Field
2. If the factory function is invoked with the parameter with_basis=None, then a free module of the given rank without distinguished basis is created.
1 sage: W = FreeModule(AA, 3, with_basis=None); W
2 3-dimensional vector space over the Algebraic Real Field
3 sage: W.category()
4 Category of finite dimensional vector spaces over Algebraic Real Field
5 sage: W.tensor_module(2, 2)
6 Free module of type-(2,2) tensors
7 on the 3-dimensional vector space over the Algebraic Real Field
It is represented by an instance of the class FiniteRankFreeModule from sage.tensor.modules. These modules are the foundation for the multilinear algebra developed by the SageManifolds project.
Connecting FiniteRankFreeModule and free modules with distinguished basis
Given a basis of a FiniteRankFreeModule, the new method isomorphism_with_fixed_basis (#30094) constructs an isomorphism from the FiniteRankFreeModule to a free module in the category ModulesWithBasis. By default, it uses a CombinatorialFreeModule:
1 sage: V = FiniteRankFreeModule(QQ, 3, start_index=1); V
2 3-dimensional vector space over the Rational Field
3 sage: basis = e = V.basis("e"); basis
4 Basis (e_1,e_2,e_3) on the 3-dimensional vector space over the
5 Rational Field
6 sage: phi_e = V.isomorphism_with_fixed_basis(basis); phi_e
7 Generic morphism:
8 From: 3-dimensional vector space over the Rational Field
9 To: Free module generated by {1, 2, 3} over Rational Field
10 sage: phi_e(e[1] + 2 * e[2])
11 e[1] + 2*e[2]
Eigenvalues and eigenvectors
Experimental functions for computing eigenvalues and eigenvectors in arbitrary precision (via Arb) including error bounds have been added. #30393
sage: from sage.matrix.benchmark import hilbert_matrix sage: mat = hilbert_matrix(3).change_ring(CBF) sage: mat.eigenvalues() [[1.40831892712365 +/- 7.16e-15] + [+/- 2.02e-15]*I, [0.12232706585391 +/- 6.49e-15] + [+/- 2.02e-15]*I, [0.00268734035577 +/- 5.60e-15] + [+/- 2.02e-15]*I]
Solving generalized eigenvalue problems Av = λBv for two square matrices A, B over RDF or CDF is now supported (via SciPy) #29243. A generalized eigenvalue λ is defined to be a root of the polynomial det(A - λ B) if this polynomial is not constantly zero.
sage: A = matrix.identity(RDF, 2) sage: B = matrix(RDF, [[3, 5], [6, 10]]) sage: D, V = A.eigenmatrix_right(B); D # tol 1e-14 [0.07692307692307694 0.0] [ 0.0 +infinity] sage: λ = D[0, 0] sage: v = V[:, 0] sage: (A * v - B * v * λ).norm() < 1e-14 True sage: A.eigenvalues(B, homogeneous=True) [(0.9999999999999999, 13.000000000000002), (0.9999999999999999, 0.0)]
Other improvements
Sage 9.2 has also merged a number of improvements to sage.tensor.modules: #30094, #30169, #30179, #30181, #30194, #30250, #30251, #30254, #30255, #30287
Polyhedral geometry
New features
It is now possible to choose which backend to use to compute regions of hyperplane arrangements 29506:
It is now possible to compute the slack matrix of a polyhedron 29838:
It is now possible to apply an affine transformation on a polyhedron 30327:
1 sage: M = random_matrix(QQ,3,3)
2 sage: v = vector(QQ,(1,2,3))
3 sage: F = AffineGroup(3, QQ)
4 sage: f = F(M, v); f
5 [ 0 0 -2] [1]
6 x |-> [ 0 1 0] x + [2]
7 [ -1 -1 1/2] [3]
8 sage: cube = polytopes.cube()
9 sage: f * cube
10 A 3-dimensional polyhedron in QQ^3 defined as the convex hull of 8 vertices
11 sage: f(cube) # also works
12 A 3-dimensional polyhedron in QQ^3 defined as the convex hull of 8 vertices
Implementation improvements
- It is now possible to set up polyhedra with both Vrep and Hrep in the following constructions:
The generation of regions of hyperplane arrangement has been improved 29661
Ehrhart related functions are now cached 29196
Obtaining incidence matrix and combinatorial polyhedron is much faster for integer and rational polyhedra 29837, 29841
The test coverage for the various backends for polyhedral computations has been improved by using _test_... methods to the abstract base class Polyhedron_base, in addition to doctests. See Meta-ticket #29842 Run a more stable test suite on polyhedra.
The face lattice can be obtained in reasonable time and no longer leaks memory 28982
There are also some bug fixes and other improvements. For more details see the release notes for optimization and polyhedral geometry software interactions in Sage.
Combinatorics
Reduction from Dancing links to SAT or MILP
It is now possible to solve an instance of an exact cover problem using a reduction from a dancing links instance to SAT 29338 or MILP 29955:
1 sage: from sage.combinat.matrices.dancing_links import dlx_solver
2 sage: rows = [[0,1,2], [3,4,5], [0,1], [2,3,4,5], [0], [1,2,3,4,5]]
3 sage: d = dlx_solver(rows)
4 sage: d.one_solution()
5 [1, 0]
6 sage: d.one_solution_using_sat_solver('cryptominisat')
7 [2, 3]
8 sage: d.one_solution_using_sat_solver('glucose')
9 [2, 3]
10 sage: d.one_solution_using_sat_solver('glucose-syrup')
11 [2, 3]
12 sage: d.one_solution_using_sat_solver('picosat')
13 [4, 5]
14 sage: d.one_solution_using_milp_solver()
15 [0, 1]
16 sage: d.one_solution_using_milp_solver('Gurobi')
17 [0, 1]
Polyomino tilings
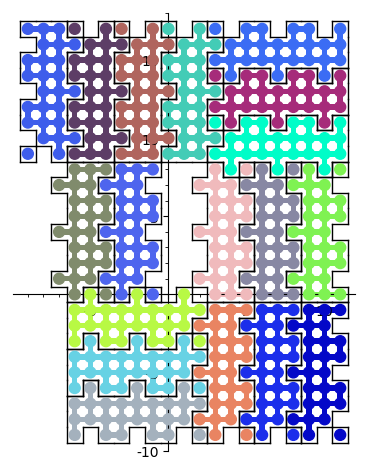
It is now possible to find a surrounding of a polyomino with copies of itself, see 29160. This is based on the dancing links solver in Sage. This is motivated by the Heesch's problem. An example is below:
sage: from sage.combinat.tiling import Polyomino sage: H = Polyomino([(-1, 1), (-1, 4), (-1, 7), (0, 0), (0, 1), (0, 2), ....: (0, 3), (0, 4), (0, 5), (0, 6), (0, 7), (0, 8), (1, 1), (1, 2), ....: (1, 3), (1, 4), (1, 5), (1, 6), (1, 7), (1, 8), (2, 0), (2, 2), ....: (2, 3), (2, 5), (2, 6), (2, 8)]) sage: H.show2d()
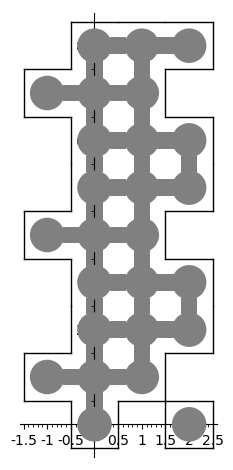
sage: %time solution = H.self_surrounding(10, ncpus=8) CPU times: user 1.69 s, sys: 1.08 s, total: 2.77 s Wall time: 3.85 s sage: G = sum([p.show2d() for p in solution], Graphics()) sage: G
Fully commutative elements of Coxeter groups
It is now possible by 30243 to enumerate and work with the fully commutative elements of a Coxeter group. Methods to compute *star operations* and plot the *heaps* of such elements are also included.
1 sage: A3 = CoxeterGroup(['A', 3])
2 sage: FCA3 = A3.fully_commutative_elements()
3 sage: FCA3.category()
4 Category of finite enumerated sets
5 sage: FCA3.list()
6 [[],
7 [1],
8 [2],
9 ...
10 [1, 3, 2],
11 [1, 2, 3],
12 [2, 1, 3, 2]]
13 sage: B8 = CoxeterGroup(['B', 8])
14 sage: FCB8 = B8.fully_commutative_elements()
15 sage: len(FCB8) # long time (7 seconds)
16 14299
17 sage: B6 = CoxeterGroup(['B', 6])
18 sage: FCB6 = B6.fully_commutative_elements()
19 sage: w = FCB6([1, 6, 2, 5, 4, 6, 5])
20 sage: w.coset_decomposition({5, 6})
21 ([6, 5, 6], [1, 2, 4, 5])
22 sage: w.star_operation({5,6}, 'lower')
23 [1, 5, 2, 4, 6, 5]
24 sage: FCB6([3, 2, 4, 3, 1]).plot_heap()
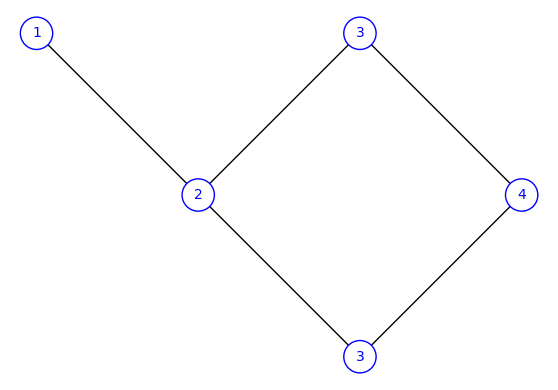
BIBDs with lambda>1
Sage can now construct a number of balanced incomplete block designs (BIBDs) with lambda>1, in particular, all the known biplanes (i.e. symmetric BIBDs with lambda=2).
Finite generalized polygons
Sage can now construct generalized quadrangles, hexagons, and octagons, and generalized quadrangles with a spread.
Graph theory
Distance regular graphs generators
A small database of constructions for distance regular graphs is now available. 15 sporadic distance regular graphs and 8 infinite families can now be constructed. Now Sage is capable of constructing all known families of distance-regular graphs with unbounded diameter.
Some code examples:
Diameter, radius, eccentricities
State-of-the-art algorithms for computing the diameter, the radius and the eccentricities of (directed) (weighted) graphs are now available 29657.
1 sage: G = graphs.RandomBarabasiAlbert(10000, 2)
2 sage: %time G.diameter(algorithm='DHV') # now default for undirected unweighted graphs
3 CPU times: user 74.4 ms, sys: 2.81 ms, total: 77.2 ms
4 Wall time: 75.8 ms
5 9
6 sage: %time G.diameter(algorithm='BFS')
7 CPU times: user 573 ms, sys: 4.04 ms, total: 577 ms
8 Wall time: 576 ms
9 9
More constructions
linear codes got a function to compute its coset graph; undirected graphs got a method to quickly compute their antipodal quotients.
More iterators
Some methods have been turned to iterators to avoid returning long lists 23002, 30470.
1 sage: g = graphs.PathGraph(5)
2 sage: bridges = g.bridges()
3 sage: next(bridges)
4 (3, 4, None)
5 sage: next(bridges)
6 (2, 3, None)
7 sage: next(bridges)
8 (1, 2, None)
9 sage: next(bridges)
10 (0, 1, None)
11 sage: next(bridges)
12 ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
13 StopIteration Traceback (most recent call last)
14 <ipython-input-38-cf858e1a0a30> in <module>
15 ----> 1 next(bridges)
16
17 StopIteration:
Implementation improvements
Truly linear time implementation of lex_BFS 11736
- Faster and memory efficient implementation for computing the distances distribution, Wiener index and Szeged index. These new implementations have linear memory consumption rather than quadratic.
We started improving the backends to speed up basic operations (edge and vertex iterations, subgraph, etc.). More to come for next release 28895.
Commutative algebra
Laurent polynomials
Rings of Laurent polynomials now support ideal creation and manipulation 29512:
sage: L.<x,y,z> = LaurentPolynomialRing(QQ, 3) sage: I = L.ideal([(x+y+z)^3+x*y, x^2+y^2+z^2]) sage: I.groebner_basis() (y^4 + 4*x*y*z^2 + y^2*z^2 + 2*x*z^3 + 2*y*z^3 - z^4 + 3/2*x*y*z + 1/4*x*z^2 + 1/4*y*z^2 - 1/4*z^3 + 1/8*x*y, x*y^2 - y^3 + 3*x*y*z + x*z^2 - z^3 + 1/2*x*y, x^2 + y^2 + z^2) sage: (x^3+y^3+z^3) in I False sage: x + x^-1*y^2 + x^-1*z^2 in I True
Motivic multiple zetas
The ring of motivic multiple zeta values has been implemented, using algorithms of Francis Brown. It allows to compute at least up to weight 12 22713.
sage: Multizeta(1,2)**2 12*ζ(1,1,1,3) + 6*ζ(1,1,2,2) + 2*ζ(1,2,1,2) sage: Multizeta(1,2)==Multizeta(3) True sage: Multizeta(2,3,4).n(100) 0.0029375850405618494701189454256
The numerical evaluation is based on PARI implementation.
Power series
There is a new method to compute the coefficients in the Jacobi continued fraction expansion of a power series 29789.
sage: t = QQ[['t']].0 sage: f = sum(factorial(n)*t**n for n in range(20)).O(20) sage: f.jacobi_continued_fraction() ((-1, -1), (-3, -4), (-5, -9), (-7, -16), (-9, -25), (-11, -36), (-13, -49), (-15, -64), (-17, -81))
Ring homomorphisms
For many polynomial ring homomorphisms, the methods inverse, is_invertible, is_injective, is_surjective, kernel and inverse_image have been implemented. This covers not only polynomial rings, but also quotient rings, number fields and Galois fields. #9792 #29723
sage: R.<x,y,z> = QQ[]
sage: sigma = R.hom([x - 2*y*(z*x+y^2) - z*(z*x+y^2)^2, y + z*(z*x+y^2),
z], R)
sage: tau = sigma.inverse(); tau
Ring endomorphism of Multivariate Polynomial Ring in x, y, z over
Rational Field
Defn: x |--> -y^4*z - 2*x*y^2*z^2 - x^2*z^3 + 2*y^3 + 2*x*y*z + x
y |--> -y^2*z - x*z^2 + y
z |--> z
sage: (tau * sigma).is_identity()
TrueThe method inverse_image can be used to test whether an element is contained in a subalgebra:
sage: R.<s,t> = PolynomialRing(QQ) sage: S.<x,y,z,w> = PolynomialRing(QQ) sage: f = S.hom([s^4, s^3*t, s*t^3, t^4], R) sage: f.inverse_image(R.ideal(0)) Ideal (y*z - x*w, z^3 - y*w^2, x*z^2 - y^2*w, y^3 - x^2*z) of Multivariate Polynomial Ring in x, y, z, w over Rational Field sage: f.inverse_image(s^3*t^4*(s+t)) x*w + y*w sage: f.inverse_image(s^2*t^2) ... ValueError: element s^2*t^2 does not have preimage
Manifolds
diff function for exterior derivatives
It is now possible to invoke diff to compute the differential (exterior derivative) of a differentiable form (#29953). For instance, for a scalar field:
sage: M = Manifold(2, 'M') sage: X.<x,y> = M.chart() sage: f = M.scalar_field(x^2*y, name='f') sage: diff(f) 1-form df on the 2-dimensional differentiable manifold M sage: diff(f).display() df = 2*x*y dx + x^2 dy
and for a 1-form:
sage: a = M.one_form(-y, x, name='a'); a.display() a = -y dx + x dy sage: diff(a) 2-form da on the 2-dimensional differentiable manifold M sage: diff(a).display() da = 2 dx/\dy
Dot and cross products of vector fields along a curve
The methods dot_product(), cross_product() and norm() can be now be used for vector fields defined along a differentiable map, the codomain of which is a Riemannian manifold (#30318). Previously, these methods worked only for vector fields on a Riemannian manifold, i.e. along the identity map. An important subcase is of course that of a curve in a Riemannian manifold. For instance, let us consider a helix C in the Euclidean space E3 parametrized by its arc length s:
sage: E.<x,y,z> = EuclideanSpace() sage: R.<s> = RealLine() sage: C = E.curve((2*cos(s/3), 2*sin(s/3), sqrt(5)*s/3), (s, -oo, +oo), ....: name='C') sage: C.display() C: R --> E^3 s |--> (x, y, z) = (2*cos(1/3*s), 2*sin(1/3*s), 1/3*sqrt(5)*s)
The tangent vector field T=C' has a unit norm since the parameter s is the arc length:
sage: T = C.tangent_vector_field() sage: T.display() C' = -2/3*sin(1/3*s) e_x + 2/3*cos(1/3*s) e_y + 1/3*sqrt(5) e_z sage: norm(T) Scalar field |C'| on the Real interval (0, 6*pi) sage: norm(T).expr() 1
We introduce the unit normal vector N via the derivative of T:
sage: T_prime = R.vector_field([diff(T[i], s) for i in E.irange()], dest_map=C, ....: name="T'") sage: N = T_prime / norm(T_prime) sage: N.display() -cos(1/3*s) e_x - sin(1/3*s) e_y
and we get the binormal vector B as the cross product of T and N:
sage: B = T.cross_product(N) sage: B Vector field along the Real number line R with values on the Euclidean space E^3 sage: B.display() 1/3*sqrt(5)*sin(1/3*s) e_x - 1/3*sqrt(5)*cos(1/3*s) e_y + 2/3 e_z
We can then form the Frenet-Serret frame:
sage: FS = R.vector_frame(('T', 'N', 'B'), (T, N, B),
....: symbol_dual=('t', 'n', 'b'))
sage: FS
Vector frame (R, (T,N,B)) with values on the Euclidean space E^3and check that it is orthonormal:
sage: matrix([[u.dot(v).expr() for v in FS] for u in FS]) [1 0 0] [0 1 0] [0 0 1]
The Frenet-Serret formulas, expressing the curvature and torsion of C, are obtained as:
sage: N_prime = R.vector_field([diff(N[i], s) for i in E.irange()], ....: dest_map=C, name="N'") sage: B_prime = R.vector_field([diff(B[i], s) for i in E.irange()], ....: dest_map=C, name="B'") sage: for v in (T_prime, N_prime, B_prime): ....: v.display(FS) ....: T' = 2/9 N N' = -2/9 T + 1/9*sqrt(5) B B' = -1/9*sqrt(5) N
Orientability of manifolds and vector bundles
It is now possible to define an orientation on a differentiable manifold and on a vector bundle (#30178). Orientations of topological manifolds have also been introduced, according to this definition.
Euclidean spaces as metric spaces
Euclidean spaces have been endowed with a distance function and have been set in the category of complete metric spaces (#30062):
sage: E.<x,y> = EuclideanSpace() sage: p = E((1,0)) # the point of coordinates (1,0) sage: q = E((0,2)) # the point of coordinates (0,2) sage: d = E.dist # the distance function sage: d(p,q) sqrt(5) sage: p.dist(q) sqrt(5) sage: E.category() Join of Category of smooth manifolds over Real Field with 53 bits of precision and Category of complete metric spaces
Bundle connections
Bundle connections have been improved (#30208) and their action on vector fields and sections has been implemented (#30209).
Internal code improvements and bug fixes
Many improvements/refactoring of the code have been performed in this release:
In addition, various bugs have been fixed: #30108, #30112, #30191, #30275, #30289, #30320, #30401, #30519.
Algebra
Lie Conformal Algebras
Implemented Lie conformal algebras and superalgebras. Here are some examples of their usage:
sage: V = lie_conformal_algebras.Virasoro(QQ); V
The Virasoro Lie conformal algebra over Rational Field
sage: V.inject_variables()
Defining L, C
sage: L.bracket(L)
{0: TL, 1: 2*L, 3: 1/2*C}
sage: L.T(2).bracket(L)
{2: 2*TL, 3: 12*L, 5: 10*C}
sage: V = lie_conformal_algebras.NeveuSchwarz(QQ)
sage: V.some_elements()
[L, G, C, TG, TG + 4*T^(2)G, 4*T^(2)G]
sage: W = lie_conformal_algebras.FreeFermions(QQbar, 2); W
The free Fermions super Lie conformal algebra with generators (psi_0, psi_1, K) over Algebraic Field
sage: W.inject_variables()
Defining psi_0, psi_1, K
sage: psi_0.bracket(psi_1.T())
{}
sage: psi_0.bracket(psi_0.T())
{1: K}
sage: psi_0.is_even_odd()
1For documentation on implemented features see Lie Conformal Algebra. For a list of implemented examples see Lie Conformal Algebra Examples.
Differential Weyl algebra
The action of differential operators from the Weyl algebra on polynomials has been implemented #29928:
sage: W.<x,y> = DifferentialWeylAlgebra(QQ) sage: dx, dy = W.differentials() sage: dx.diff(x^3) 3*x^2 sage: (x*dx + dy + 1).diff(x^4*y^4 + 1) 5*x^4*y^4 + 4*x^4*y^3 + 1
Improved Unicode support
Unicode identifiers
Python 3 made much improved support for Unicode available, and Sage 9.2 has merged several Unicode improvements. Note that Python does not allow arbitrary Unicode characters in identifiers but only word constituents. So before you get excited about using emojis... note that they cannot be used:
However, we can use letters from various alphabets. The updated IPython allows us to type them using latex and unicode tab completion:
1 sage: μ, ν, ξ = 1, 2, 3 # type \mu<TAB>,
2 # \nu<TAB>, ...
3 sage: SR('λ + 2λ')
4 3*λ
5 sage: var('α', domain='real')
6 α
7 sage: Ш = EllipticCurve('389a').sha()
8 # type \CYR<TAB> CAP<TAB>
9 # LET<TAB> SHA<TAB><ENTER>
10 sage: Ш
11 Tate-Shafarevich group for the Elliptic Curve
12 defined by y^2 + y = x^3 + x^2 - 2*x over Rational Field
13 sage: GelʹfandT͡setlinPattern = GelfandTsetlinPattern
14 # type \MODIFIER LETTER
15 # PRIME<TAB><ENTER>
16 # for the romanized soft mark
17 sage: ГельфандЦетлинPattern = GelʹfandT͡setlinPattern
18 sage: ГельфандЦетлинPattern([[3, 2, 1], [2, 1], [1]]).pp()
19 3 2 1
20 2 1
21 1
22 sage: 四次方(x) = x^4
23 sage: 四次方(3)
24 81
We can use math accents...
... and have fun with modifier letters:
1 sage: ℚ̄ = QQbar # type \bbQ<TAB>\bar<TAB>
2 sage: %display unicode_art
3 sage: A = matrix(ℚ̄, [[1, 2*I], [3*I, 4]]); A
4 ⎛ 1 2*I⎞
5 ⎝3*I 4⎠
6 sage: Aᵀ = A.transpose() # type A\^T<TAB><ENTER>
7 sage: Aᵀ
8 ⎛ 1 3*I⎞
9 ⎝2*I 4⎠
10 sage: Aᴴ = A.conjugate_transpose()
11 # type A\^H<TAB><ENTER>
12 sage: Aᴴ
13 ⎛ 1 -3*I⎞
14 ⎝-2*I 4⎠
15 sage: C = Cone([[1, 1], [0, 1]])
16 sage: Cᵒ = C.dual(); Cᵒ # type C\^o<TAB><ENTER>
17 2-d cone in 2-d lattice M
But note that Python normalizes identifiers, so the following variants are not distinguished:
1 sage: AT == Aᵀ, AH == Aᴴ, Co == Cᵒ
2 (True, True, True)
3 sage: ℚ = QQ # type \bbQ<TAB><ENTER>
4 sage: ℚ
5 Rational Field
6 sage: Q = 42
7 sage: ℚ
8 42
9 sage: F = 1
10 sage: 𝐹, 𝐅, 𝓕, 𝕱, 𝗙, 𝘍, 𝙁, 𝙵 # type \itF<TAB>, \bfF<TAB>,
11 # \scrF<TAB>, \frakF<TAB>,
12 # \sansF<TAB>, ...
13 (1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1)
We have also added a few Unicode aliases for global constants and functions.
See Meta-ticket #30111: Unicode support for more information.
Unicode characters allowed in tensor index notation
Greek letters (and more generally any Unicode non-digit word-constituent character) are now allowed in index notation for tensors (#29248). For instance, taking the trace of a type-(1,1) tensor field:
sage: E.<x,y> = EuclideanSpace() sage: t = E.tensor_field(1, 1, [[x, 1], [0, y]]) sage: t['^μ_μ'] Scalar field on the Euclidean plane E^2 sage: t['^μ_μ'] == t.trace() True
Unicode art
#30119 Implemented a general function for writing integers as unicode sub/superscripts.
In #29205, some Lie algebra elements now have better unicode support:
sage: L = LieAlgebra(QQ, cartan_type="A2", representation='matrix') sage: unicode_art(L.an_element()) ⎛ 1 1 0⎞ ⎜ 1 0 1⎟ ⎝ 0 1 -1⎠ sage: L = lie_algebras.Heisenberg(QQ, 2) sage: unicode_art(sum(L.basis())) p₁ + p₂ + q₁ + q₂ + z sage: L = lie_algebras.VirasoroAlgebra(QQ) sage: unicode_art(L.an_element()) d₋₁ + d₀ - 1/2 + c sage: L = LieAlgebra(QQ, cartan_type=['A',1,1]) sage: unicode_art(L.an_element()) ( alpha[1] + alphacheck[1] + -alpha[1] )⊗t⁰ + ( -alpha[1] )⊗t¹ + ( alpha[1] )⊗t⁻¹ + c + d sage: L.<x,y> = LieAlgebra(QQ) sage: unicode_art(x.bracket(y)) [x, y] sage: L = LieAlgebra(QQ, cartan_type=['A',2], representation="compact real") sage: unicode_art(L.an_element()) ⎛ i i + 1 i + 1⎞ ⎜i - 1 i i + 1⎟ ⎝i - 1 i - 1 -2*i⎠
As part of #29696, Temperley-Lieb diagrams now have unicode (and ascii) art:
sage: from sage.combinat.diagram_algebras import TL_diagram_ascii_art sage: TL = [(-15,-12), (-14,-13), (-11,15), (-10,14), (-9,-6), ....: (-8,-7), (-5,-4), (-3,1), (-2,-1), (2,3), (4,5), ....: (6,11), (7, 8), (9,10), (12,13)] sage: TL_diagram_ascii_art(TL, use_unicode=False) o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o | `-` `-` | `-` `-` | `-` | | | `---------` | | | .-------` | `---. | .-------` | .-----. | | .-----. .-. | .-. | .-. | | | | .-. | o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o sage: TL_diagram_ascii_art(TL, use_unicode=True) ⚬ ⚬ ⚬ ⚬ ⚬ ⚬ ⚬ ⚬ ⚬ ⚬ ⚬ ⚬ ⚬ ⚬ ⚬ │ ╰─╯ ╰─╯ │ ╰─╯ ╰─╯ │ ╰─╯ │ │ │ ╰─────────╯ │ │ │ ╭───────╯ │ ╰───╮ │ ╭───────╯ │ ╭─────╮ │ │ ╭─────╮ ╭─╮ │ ╭─╮ │ ╭─╮ │ │ │ │ ╭─╮ │ ⚬ ⚬ ⚬ ⚬ ⚬ ⚬ ⚬ ⚬ ⚬ ⚬ ⚬ ⚬ ⚬ ⚬ ⚬
Configuration and build changes
Initial configuration with ./configure required
Sage 9.1 introduced informational messages at the end of a ./configure run regarding system packages. To make sure that these messages are not overlooked, Sage 9.2 no longer invokes ./configure when you type make in an unconfigured source tree. See sage-devel: require "./configure" before "make", #29316.
Support for gcc/gfortran 10.x added
All standard Sage packages have been upgraded in Sage 9.2 so that they build correctly using gcc/gfortran 10.x. The Sage ./configure script therefore now accepts these compiler versions.
Selecting a system Python to use for Sage's venv
The configure script in Sage 9.2 has been changed so it only looks for a binary named python3 in your PATH. If Sage cannot find a suitable python3 in your PATH, it will build its own copy of Python 3.8.5. Sage no longer looks for versioned Python binaries such as python3.7, #30546.
To configure Sage to use a specific Python installation, you can use ./configure --with-python=/path/to/python3. The configure script will test whether this installation is suitable for Sage and will exit with an error otherwise.
System package information for more distributions
System package information has been added for Gentoo Linux, FreeBSD, Void Linux, and NixOS.
System package information for optional packages at runtime
When a user tries to use a feature depending on an optional package is not installed, Sage now issues advice regarding the packages that should be installed to provide the feature -- using either the system package manager, pip, or (in the Sage distribution) sage -i #30606.
(For packagers: For this to work, either SAGE_ROOT/build/pkgs/*/distros/ and SAGE_ROOT/build/bin/{sage-get-system-packages, sage-guess-package-system, sage-print-system-package-command} need to be installed, or alternative implementations of these scripts need to be provided.)
For developers: Changes to the build system of sagelib
Let's talk about setup.py. The build system of the Sage library, in build/pkgs/sagelib/src/setup.py, is based on distutils (not setuptools); it is implemented in the package sage_setup. In particular, it implements its own version of source code discovery methods similar to setuptools.find_packages: sage_setup.find.find_python_sources. Because of source discovery, developers can add new Python modules and packages under src/sage/ simply by creating files and directories; it is not necessary to edit setup.py.
Prior to Sage 9.2, the situation was different for Cython extensions. They had to be listed in src/module_list.py, either one by one, or using glob patterns such as * and **. Sage 9.2 has eliminated the need for src/module_list.py by extending sage_setup.find.find_python_sources; it now also finds Cython modules in the source tree (Trac #29701).
Some Cython modules need specific compiler and linker flags. Sage 9.2 has moved all of these flags from Extension options in src/module_list.py to distutils: directives in the individual .pyx source files, see #29706 and Cython documentation.
Sage 9.2 has also changed the mechanism for conditionalizing a Cython extension module on the presence of a Sage package. Consider the module sage.graphs.graph_decompositions.tdlib as an example. Prior to Sage 9.2, this module was declared as an OptionalExtension, conditional on the SPKG tdlib, in src/module_list.py. The new mechanism is as follows. src/setup.py maps the SPKG name tdlib to the "distribution name" sage-tdlib. At the top of the Cython source file src/sage/graphs/graph_decompositions/tdlib.pyx, there is a new directive sage_setup: distribution = sage-tdlib. Now the source discovery in sage_setup.find.find_python_sources includes this Cython module only if the SPKG tdlib is installed and current.
New development tools
Testing and linting with tox
tox is a popular package that is used by a large number of Python projects as the standard entry point for testing and linting.
Sage 9.1 started to use tox for portability testing of the Sage distribution, which requires an installation of tox in the system python.
Sage 9.2 has added a tox configuration (src/tox.ini) for the (more typical) use of tox for testing and linting of the Sage library #30453. This provides an entry point for various testing/linting methods that is more idiomatic from the viewpoint of the Python community.
The commands sage -t, sage -coverage, sage -coverageall, and sage -startuptime are repackaged as sage --tox, as the following output from sage -advanced indicates:
$ ./sage -advanced
SageMath version 9.2
...
Testing files:
...
--tox [options] <files|dirs> -- general entry point for testing
and linting of the Sage library
-e <envlist> -- run specific test environments (default: run all)
doctest -- run the Sage doctester
(same as "sage -t")
coverage -- information about doctest coverage of files
(same as "sage --coverage[all]")
startuptime -- display how long each component of Sage
takes to start up
(same as "sage --startuptime")Three new linting methods are added:
pycodestyle -- check against the Python style conventions of PEP8
relint -- check whether some forbidden patterns appear
(includes all patchbot pattern-exclusion plugins)
codespell -- check for misspelled words in source codeThis functionality is available after installing the optional tox package using sage -i tox (or having tox available in the system).
Reusable wheels for the Python packages built by the Sage distribution
Sage 9.2 has changed the build process of all Python packages in the Sage distribution so that wheels are built and stored in $SAGE_LOCAL/var/lib/sage/wheels/ #29500.
Users can install these wheels into virtual environments that use the same base python version, using standard tools such as pip install --find-links. Example:
$ local/bin/python3 -m venv some-venv $ cd some-venv/ $ bin/pip3 install -v --no-index --find-links=../local/var/lib/sage/wheels/ Pillow
The installation is very fast because it does not involve compilation.
Note: Many of these wheels include extension modules that refer to libraries in the Sage installation in $SAGE_LOCAL with hard-coded paths. Therefore the wheels are not immediately suitable for distribution.
Cleaning
#29636: Delete changelog sections from all SPKG information files; they were deprecated in favor of using Trac years ago. The contributions of Sage developers maintaining SPKGs are documented by our historical changelogs.
Removing support for Python 2 allowed us to remove several backport packages in #29754
We also removed the deprecated SageNB (superseded a long time ago by the Jupyter notebook) in #29754 and several of its dependencies. For converting old Sage worksheet files (*.sws), the script sage -sws2rst is available. (In Sage 9.0 and 9.1, it was available only in Python 2 builds of Sage; in #28838, it was ported to Python 3.)
Support for installing "old-style Sage packages" (.spkg files), deprecated in Sage 6.9, has been removed in #29289, after making the last two missing packages, cunningham_tables and polytopes_db_4d, available as normal optional Sage packages. Users who wish to package their own Sage code for distribution may find a list of external packages helpful, many of which follow best practices in packaging.
The use of sage.misc.package has been essentially eliminated from the Sage library by transitioning to sage.feature; see #30607, #30616.
Availability of Sage 9.2 and installation help
SageMath 9.2 was released on 2020-10-24; it is available in the sage git repository, and the self-contained source tarballs are available for download.
Sage 9.2 has been tested to compile from source on a wide variety of platforms, including:
- Linux 64-bit (x86_64)
- ubuntu-{trusty,xenial,bionic,eoan,focal,groovy},
- debian-{jessie,stretch,buster,bullseye,sid},
- linuxmint-{17,18,19,19.3},
- fedora-{26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33},
- centos-{7,8},
- archlinux,
- slackware-14.2,
- conda-forge
- Linux 32-bit (i386)
- debian-buster
- ubuntu-eoan
- macOS
- macOS Catalina and older (macOS 10.x, with Xcode 11.x or Xcode 12)
- optionally, using Homebrew
- optionally, using conda-forge
note that macOS 11 beta ("Big Sur") is not supported
- Windows (Cygwin-64).
Binaries
- TBA
Availability in distributions
Installation FAQ
See README.md in the source distribution for installation instructions.
See sage-release, sage-devel.
