|
Size: 27056
Comment:
|
Size: 28512
Comment:
|
| Deletions are marked like this. | Additions are marked like this. |
| Line 11: | Line 11: |
| [[TableOfContents(2)]] | See also the [[http:/combinat/MercurialBasic|basic instructions]]. Temporary: http://blog.phasing.org:993 <<TableOfContents(2)>> |
| Line 14: | Line 19: |
| attachment:patch-server.png If you have some ideas to improve this picture. Here is the xfig file: attachment:patch-server.fig |
{{attachment:patch-server.png}} If you have some ideas to improve this picture. Here is the xfig file: [[attachment:patch-server.fig]] |
| Line 83: | Line 88: |
| $ hg pop # Unapply the most recently applied patch | $ hg qpop # Unapply the most recently applied patch |
| Line 115: | Line 120: |
| Before pulling changes from the server, it is a good idea to save your current working state, by {{{qrefresh}}}ing any patch that you are currently editing, and then {{{qcommit}}}ing all of the changes you have made. Then, from the {{{PATCHES}}} directory you can execute the command {{{$ hg pull }}}. This will examine all changesets in the secondary repository on the server, and will download any changesets that are found which you do not already have locally. One of two things will happen when you run this command. Either no new changesets will be found, or some changesets will be found and downloaded. Mercurial will tell you which of these occurred. In the case that no new changesets are found, there is nothing more to do. If changesets were found, you need to run the command {{{$ hg update }}} to commit and apply them. There are two possible results to this command. The first is that the update will be successful and Mercurial will respond with a line like |
Before pulling changes from the server, it is a good idea to save your current working state, by {{{qrefresh}}}ing any patch that you are currently editing. Then, from the {{{PATCHES}}} directory you can execute the command {{{$ hg pull -u}}}. This will examine all changesets in the secondary repository on the server, and will download any changesets that are found which you do not already have locally, and try to update accordingly your collection of patches. TODO The first is that the update will be successful and Mercurial will respond with a line like |
| Line 155: | Line 162: |
| Line 179: | Line 187: |
| You want to use the [http:/combinat/MercurialBasic sage-combinat script] | You want to use the [[http:/combinat/MercurialBasic|sage-combinat script]] |
| Line 185: | Line 193: |
| See the [http:/combinat/MercurialBasic simple instructions] | See the [[http:/combinat/MercurialBasic|simple instructions]] |
| Line 207: | Line 215: |
| Line 209: | Line 219: |
| Go to the sage-combinat directory, and make sure there is no local changes: | Go to the sage-combinat directory, and make sure that there is no local changes (hg status); otherwise dicard them or save them in your favorite patch (hg qrefresh). |
| Line 215: | Line 226: |
| Apply all patches, and make sure that everything is fine: {{{ |
Pull the latest version of the patches from the server, and make sure that everything is fine after applying all patches: {{{ sage -combinat update -f |
| Line 221: | Line 233: |
| hg qcommit }}} Pull changes from server as described in the example above. If changes are found, begin this process again. Otherwise, stop 10s for breathing and: |
}}} The -f is to tell sage -combinat to run even if your patch directory is modified, which it probably is. When pulling from the server, your changes will be merged with those from the server. You may get conflicts in the series file, or patches that do not apply anymore. Fix the patches that you own, and get in touch with the owners of the other broken patches. When everything is ready, double check that you are up to date: {{{ sage -combinat update -f }}} and then: |
| Line 227: | Line 247: |
| hg commit | |
| Line 229: | Line 250: |
In case you have been unlucky, and there has been a change on the patch server between your last pull and your commit, push will fail with an error like "abort: push creates new remote heads! did you forget to merge?". You then have to merge your local modifications with the remote ones: {{{ cd .ht/patches hg pull -u hg merge }}} If the merge goes through automatically, just commit with Merge as message, and push. Otherwise, well, feel free to ask for help! |
|
| Line 247: | Line 280: |
| === Selecting guarded patches === Some patches may be guarded since they are experimental, not yet finished, or used for different versions of sage. Guarded patches are not applied unless explicitly chosen. For example if one would like to apply patches labeled [+experimental] one can use the following steps: {{{ hg qselect experimental sage -combinat qselect }}} Then reapply the appropriate patches, typically with {{{ hg qpop -a hg qpush -a }}} To disregard all guarded patches one uses instead: {{{ hg qselect -n sage -combinat qselect }}} |
|
| Line 251: | Line 305: |
| See the [http:/combinat/MercurialBasic simple instructions] | See the [[http:/combinat/MercurialBasic|simple instructions]] |
| Line 283: | Line 337: |
= Use and Contribute to the sage-combinat tree : step by step = See also the [[http:/combinat/MercurialStepByStep|step by step instructions]] to contribute to sage-combinat. |
The Sage-combinat patch server: advanced description and instructions
The suggested process for people doing significant development to the combinat area of sage is to work in a clone of a clean version of sage (this clone is typically called sage-combinat). The files in this clone are managed with a Mercurial repository using Mercurial queues. The patch files that are created with this process are managed in a secondary Mercurial repository, which is periodically synched with the server at http://sage.math.washington.edu:2144/ . The purpose of this page is to give more detail on how this process works. General concepts are given at the top, and examples of common working situations are given at the bottom. To skip to one of these common examples, click on one of the following links.
See also the basic instructions.
Temporary: http://blog.phasing.org:993
Contents
Sage-combinat development workflow
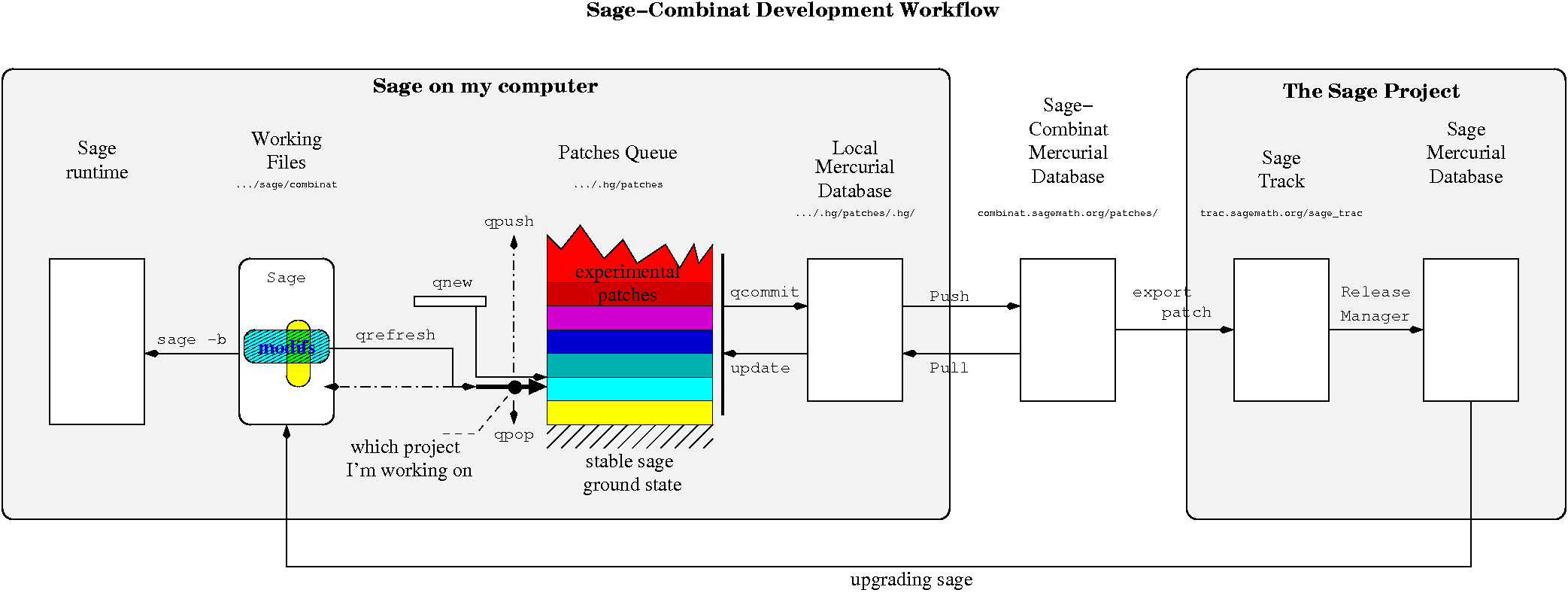
If you have some ideas to improve this picture. Here is the xfig file: patch-server.fig
Important Sage Commands
Note: Throughout this document $SAGE_ROOT is the directory where you have Sage installed.
There are two important sage commands that you must be aware of as part of the development process. The first is related to the fact that editing the sage source-code files will not immediately change the behavior of sage. In order for your changes to have an effect, you must first run
$ sage -b combinat
which will rebuild combinat branch of sage, using the current source code files. Note that the 'combinat' argument is not necessary if the last time you ran sage you used the combinat branch. Variants of this command are $ sage -br (build and run) which will build sage and then run it, and $ sage -ba (build all) which is necessary if any Cython files have been modified.
The second important sage command to know is
$ sage -t filenames
which will run all the doctests in named files. Note that you should rebuild sage before running $ sage -t .
Managing the Primary Repository
The primary Mercurial repository manages all files contained in $SAGE_ROOT/devel/sage-combinat/ (including all subdirectories) EXCEPT the directory $SAGE_ROOT/devel/sage-combinat/.hg/patches . The files in that directory are managed by the secondary repository which is discussed below. The files in the primary repository are all the files that make sage work, so it is important to manage any changes that are made to these files. That way your changes can easily be undone, shared with other people, etc.
Patch and Queue Concepts
The primary repository is managed with a Mercurial queue of patches. A patch is information that tells Mercurial how to go back and forth between an "old version" of a collection of files and a "new version" of those files. Changing the collection from the old version to the new is called applying the patch, and the inverse is called unapplying the patch. The information about how to make this transformation is stored in a text file with a .patch extension. For our project, all patch files live in the directory $SAGE_ROOT/devel/sage-comibinat/.hg/patches . Since these are just text files, they are easy to manually inspect with less or any text editor. Manually editing these files, however, is strongly discouraged.
Our project consists of many patches, and these patches are managed with a Mercurial queue. A queue can be thought of as a "stack" of patches. Every change that we make to sage should belong to a patch, and every patch should belong to the queue. If, from any subdirectory of $SAGE_ROOT/devel/sage-combinat/ (except .hg/patches ), you type the command $ hg qseries you will see a list of patches in the queue. These patches are ordered, with the first in the list being the first patch which is applied to the base version of sage. Mercurial stores the series in the text file $SAGE_ROOT/devel/sage-comibinat/.hg/patches/series . If for some reason you want to change the order in which these patches are applied, it is possible to edit this file manually; this is not generally recommended. (It may be necessary, however, when updating the secondary repository; see below for more details). It is important to realize that not all of the patches in the series are necessarily currently applied. You can see which of the patches are currently applied with the command $ hg qapplied , or just get the name of the last patch applied with the command $ hg qtop .
What makes working with Mercurial queues so nice, is that it makes applying and unapplying patches very, very easy. Specifically, the command $ hg qpop will unapply the patch currently on the top of the stack, and $ hg qpush will apply the next patch in the series that is not currently applied. The variants $ hg qpop -a and $ hg qpush -a will unapply and apply (respectively) all patches in the series. So, for example, if you type $ hg qpop -a all files will revert to their state as of the base version of sage. You can now rebuild and run sage to see sage as ordinary users see it. When you get bored of this and want to go back to the exciting bleeding-edge development version, it's as simple as $ hg qpush -a and $ sage -br .
Creating a new patch
This is done with the command $ hg qnew patchname.patch. Generally speaking, you should only create a new patch at the top of the stack, with all previous patches applied. In other words, you should always run $ hg qpush -a before running $ hg qnew . Furthermore, it is a good idea to synch your queue with the server (see below) before starting a new patch. After an $ hg qnew , you will see the new patch as the top patch with $ hg qseries , $ hg qapplied , and $ hg qtop .
The following is a suggested naming convention:
<theme>_<feature/fix>_<trac ref if any>_<rev if any>_<owner or final or closed>.patch
Examples:
- root_systems_lattices_nt.patch
- partitions_fix_3244_mh.patch
- crystals_affine_as.patch
- free_modules_1_mh.patch
- free_modules_2_mh.patch
- free_modules_final.patch
- dyck_words_closed.patch
A series of patches like the free_modules one above is intended to be progressively folded together into a single patch free_modules.patch before submission to sage. The name free_modules_final indicates that the owner of this patch will no longer edit it, and it is ready to post to trac. The name *_closed.patch indicates that this patch has been posted to trac and the corresponding ticket has been closed.
Editing Patches
The basic idea in editing patches is that you should move the patch you want to edit to the top of the stack (using qpush, qpop, or qnew), edit the files you want to edit, then update the current patch file with the command $ hg qrefresh . If you only want to update your changes to particular files, you can do this with $ hg qrefresh -I filenames . (More options to this command can be found with $ hg help qrefresh .) Once you start editing files, Mercurial will not let you qpush or qpop until you have done a qrefresh. Obviously, you should not edit a patch in the middle of the series if you know there will be conflicts with patches later in the series. However, if you have minor changes that logically belong to a patch in the middle of the stack, it is encouraged to make your edits to that patch, as opposed to creating a new one.
It is highly recommended that you only edit your own patches. This is to prevent conflicts that will occur if multiple people simultaneously edit the same patch. Edit other people's patches only with their explicit permission.
If in your editing process you create or delete files, you must give this information to Mercurial. This is done with the commands $ hg add filename and $ hg remove filename , respectively.
Since it is easy to forget your current state of editing, Mercurial provides commands to show you what you have done. The command $ hg status will show you what files you have edited since the last time you did $ hg qrefresh . The command $ hg diff will show you precisely what these changes are.
If you have made edits since your last qrefresh that you've decided you don't want, you can get rid of them with $ hg revert filenames or hg revert --all . This will take the indicated files back to their state at the time of the last qrefresh. Note that the edits since that time will be completely lost.
You may notice that our instructions to this point only provide a means for having a single saved version of any given patch. It is possible to store information about multiple versions of a single patch file; this is done with the secondary repository which is discussed in more detail below.
Quick Summary of Common Queue Commands
$ hg help -v # List all Mercurial commands (including queue commands)
$ hg help command # Provides a brief description and available options for the named command
$ hg qseries # Lists all patches in the queue, starting with the first to be applied
$ hg qapplied # Lists all patches in the queue which are currently applied
$ hg qtop # Displays the most recently applied patch
$ hg qpush # Apply the first patch in the series which is not currently applied
$ hg qpop # Unapply the most recently applied patch
$ hg qnew name.patch # Create a new patch on top of the current 'qtop'
$ hg add filename # Add a file to the Mercurial repository
$ hg remove filename # Remove a file from the Mercurial repository
$ hg status # List of files modified since last 'qrefresh'
$ hg diff # List of precise changes since last 'qrefresh'
$ hg qrefresh # Store recent changes in the current top patch
$ hg revert filenames # Lose all changes to filenames since last 'qrefresh'
$ hg remove name.patch # Completely remove the named patch from the entire queue. The patch must currently be unapplied
$ hg qrename f1.patch f2.patch # Renames f1.patch to f2.patch. The series file is updated as well
$ hg qfold a.patch # a.patch must be unapplied. This is equivalent to applying a, qrefreshing the current patch, then deleting a
# i.e., the changes described by a.patch get folded into the current top patch
Managing the Secondary Repository
At this point, you should understand how to manage your changes to the sage source files using a collection of patch files managed by a Mercurial queue. However this is not sufficient for our purposes. How do we share our patches with other developers? If we edit and save an early patch in a way that is not compatible with later patches, how can we recover? These problems are solved with the secondary Mercurial repository.
Recall that Mercurial stores all information about the queue (in particular, the individual .patch files and the series file) in the directory $SAGE_ROOT/devel/sage-comibinat/.hg/patches . For the rest of this document, we will refer to this directory as the PATCHES directory. The PATCHES directory is NOT managed by the primary repository because, in a sense, it IS the primary repository. So, we have created a secondary Mercurial repository to manage the files in this directory.
The most important point to clarify when working with both the primary and secondary repositories is: When you type a command, how does Mercurial know whether the command should be applied to the primary or secondary repository? The answer is given by the directory from which you type the command. If you are in the PATCHES directory, Mercurial will assume the command applies to the secondary repository; if you are in one of the sage source file directories, Mercurial will assume the command applies to the primary repository. The exception to this rule is the command $ hg qcommit which will be discussed in detail below.
Of course, the files in PATCHES/.hg/ are not managed by the secondary repository; they ARE the secondary repository. So, if you so desire, you can go to this directory and create a tertiary Mercurial repository. For the sake of your sanity, this is not recommended.
To manage the files in the secondary repository we do not use queues; Mercurial's base functionality is enough. Therefore, it is appropriate to describe at this point how Mercurial manages changes when NOT using queues.
Mercurial Concepts
In standard Mercurial parlance, the basic unit of change is known as a 'changeset'. A changeset is basically just another name for a patch, although changesets are typically identified by a number and not a descriptive name. If you type the command $ hg log from PATCHES you will see a list of all the changesets applied to the PATCHES directory since it was created. (It is often useful to view the log in a paging program, eg $ hg log | less , since the list of changesets can be quite long. In fact, if you look at the log for the primary repository, you will see every changeset applied to sage since version 1.0.) The most recently applied changeset is known as the tip.
The point of the secondary repository is to record changes made to the PATCHES directory, allowing us to revert those changes or merge our changes with those of other developers. Thus, we must periodically report these changes to Mercurial's secondary repository. This can be done in one of two ways: The first is to go to the PATCHES directory and then type $ hg commit. The second, which is completely equivalent, is to type $ hg qcommit from any of the sage source file directories. This command will create changeset (patch file) containing all the differences between the state of the PATCHES directory at the time of the previous commit and the current state of the PATCHES directory. When you run this command, you will be prompted for a message which will show up in the summary line of the log file. You can enter this message directly with the - m option to the commit (or qcommit) command. For example, $ hg qcommit -m "made some changes" . Of course, your message should be much more informative.
After having done a commit, the collection of changesets in the secondary repository completely describes the current state of PATCHES directory. The information in the PATCHES directory, in turn, completely describes how to get to the current development version of sage from the base version. Thus, to stay in synch with other combinat developers, it is sufficient to keep our secondary repositories in synch. If you created your sage-combinat branch according to the instruction here, your secondary repository will "know about" our central server: sage.math.washington.edu:2144 . Periodically, you will need to push the changes made to your secondary repository to this server, and likewise pull the changes on this server to your own secondary repository.
Pulling changes from the server
Before pulling changes from the server, it is a good idea to save your current working state, by qrefreshing any patch that you are currently editing. Then, from the PATCHES directory you can execute the command $ hg pull -u. This will examine all changesets in the secondary repository on the server, and will download any changesets that are found which you do not already have locally, and try to update accordingly your collection of patches.
TODO The first is that the update will be successful and Mercurial will respond with a line like
2 files updated, 0 files merged, 1 files removed, 0 files unresolved
The other possibility is that there will be a conflict when you try to upgrade. Since we all only edit our own .patch files (unless given explicit permission) the conflict is most likely with the file PATCHES/series . You will need to manually merge the two versions of this file (the version from the server and the version you had locally). Fortunately, the series file is so simple, that this is easy to do. The way to resolve conflicts with this file is to put the entire series file from the server is at beginning of the file, and any new, local, patches at the end. Depending on your system, Mercurial may launch a 'diff' program when you try to upgrade and a conflict is found. You can use this program to make the changes, or just close it and edit the file with your favorite editor. Here is an example.
PATCHES$ cat series A.patch B.patch C.patch PATCHES$ hg pull ** changes found *** PATCHES$ hg upgrade
At this point you should see a window pop up with the different versions of the series file. Suppose the version from the server looked like this:
A.patch B.patch D.patch E.patch
Then you would want to edit the series file to look like:
A.patch B.patch D.patch E.patch C.patch
and then commit this change with the command $ hg commit -m "merge" .
Finally you need to update the primary repository by going to a sage source code directory (for example, $SAGE_ROOT/devel/sage-combinat and running $ hg qpop -a followed by $ hg qpush -a . This step also has the possibility of resulting in a conflict: following the example above, your file C.patch could contain some changes which conflict with either D.patch or E.patch. If this is the case, you have two options. The first is to edit C.patch until the conflict goes away. Mercurial will show C.patch at the top of the queue, and you can use the commands from the previous section to edit this patch until the conflict goes away. The second possibility is that you can become convinced that the real problem is an error in either D or E . In this case, you should contact the author of the offending patch, and ask him or her to fix the problem and push the change back to the server. Then you can re-pull, and hopefully this time there will be no conflict.
Pushing Changes To The Server
This step is relatively simple; the hard part is making sure that your changes will apply cleanly on the server. The first step is to create or edit some patch on your local machine. If you want to push this patch to the server so that other developers can work on it, it is not necessary that all doctests pass. However, it should be the case that you can apply this patch and run $ sage -br without errors.
The next step is to pull any changes that you might not yet have from the server. This step is described in detail above. If changes were found you should merge, apply all changes to the primary repository, and make sure that everything you expect to work still works (sage -br, doctests, etc). After going through this process you should again try to pull changes from the server. If more changes come down, repeat the process.
Eventually, no changes will be found. At this point it is safe to do: PATCHES$ hg push . This should report that your changes were applied successfully to the server.
Note: You can always see the state of the server directly in your browser at: http://sage.math.washington.edu:2144/ .
Resolving Secondary Repository Problems
We've described how the secondary repository keeps track the changes to our PATCHES directory, and how we can synch with central server. Another useful tool to know is the command $ hg strip changeset-number . This command allows you to remove a particular changeset (and all changesets which depend on it) from the secondary repository. (You can not run this command if you have uncommitted changes.) We can use this command to get back to the state of any arbitrary qcommit. For example, if your system is completely fouled up, you can use the following series of commands to force your system to mirror the version currently on the server. Note: If there are any local files which you have changed (and you want to have access to those changes) you should save a copy of them outside of the sage directory structure before starting this process.
cd $SAGE_ROOT/devel/sage-combinat/.hg/patches # Go to the $PATCHES directory hg commit -m "commit uncommitted changes" # Commit uncommitted changes hg strip 0 # Completely clean the $PATCHES directory hg pull # Get the current state from the server hg update # Apply and commit server changesets to secondary repository cd ../.. # Go to a primary repository directory hg qpop -a # Unapply any applied changes hg qpush -a # Apply all the changes from the server
Examples of common situations
Downloading, installing the sage-combinat patches
You want to use the sage-combinat script
Pulling changes from server
With the sage-combinat script
See the simple instructions
By hand
Go to the sage-combinat directory, and make sure there is no local changes:
cd $SAGE_ROOT/devel/sage-combinat hg status
If there is any local modifications, they should first be saved in an appropriate patch (see section ...), or discarded before proceeding.
(FIXME: should we recommend to qcommit first, or not?)
hg qpop -a cd .hg/patches hg pull -u # Resolve conflicts with series file as described above cd ../.. hg qpush -a sage -b
Push changes to server
Example
Go to the sage-combinat directory, and make sure that there is no local changes (hg status); otherwise dicard them or save them in your favorite patch (hg qrefresh).
cd $SAGE_ROOT/devel/sage-combinat hg status
Pull the latest version of the patches from the server, and make sure that everything is fine after applying all patches:
sage -combinat update -f hg qpush -a sage -br # Make sure this works sage -t filenames # If you believe your tests should pass, check them.
The -f is to tell sage -combinat to run even if your patch directory is modified, which it probably is.
When pulling from the server, your changes will be merged with those from the server. You may get conflicts in the series file, or patches that do not apply anymore. Fix the patches that you own, and get in touch with the owners of the other broken patches.
When everything is ready, double check that you are up to date:
sage -combinat update -f
and then:
cd .hg/patches hg commit hg push
In case you have been unlucky, and there has been a change on the patch server between your last pull and your commit, push will fail with an error like "abort: push creates new remote heads! did you forget to merge?". You then have to merge your local modifications with the remote ones:
cd .ht/patches hg pull -u hg merge
If the merge goes through automatically, just commit with Merge as message, and push. Otherwise, well, feel free to ask for help!
Exporting Patches for use with trac
When a patch is ready to be applied to sage, you should first verify that it will apply cleanly. If you want to be able to undo anything you do in this step, you should run hg qcommit before beginning.
The first step is, from the PATCHES directory, manually edit the series file so that your patch (or patches) are applied only to patches labelled *_closed. Then (from the source directories) use qpush and qpop to bring the first of your patches to the top of the stack (ie, only one of your patches should be applied). Suppose your patches were called 1.patch and 2.patch, and you currently have 1.patch at the top of the stack, and 2.patch as the next patch to be applied. The command $ hg qfold 2.patch will incorporate the changes from 2.patch into 1.patch, and then delete 2.patch. You should repeat this process until all patches working on one particular issue have been incorporated.
Then you should make sure that sage builds, runs, and passes tests, with just this patch applied only to patches that have already been closed.
The next step is to export your patch for submission. Running "hg export" includes extra information in the patch such as the author of the patch.
Example
cd $SAGE_ROOT/devel/sage-combinat hg export new_feature.patch > /path/to/new_feature_for_trac.patch
You would then upload the file new_feature_for_trac.patch to the appropriate ticket on the Sage Trac server, creating the ticket if necessary. Procedures for using the trac system are described here: http://wiki.sagemath.org/TracGuidelines
Don't forget to also push your changes to the server.
Selecting guarded patches
Some patches may be guarded since they are experimental, not yet finished, or used for different versions of sage. Guarded patches are not applied unless explicitly chosen. For example if one would like to apply patches labeled [+experimental] one can use the following steps:
hg qselect experimental sage -combinat qselect
Then reapply the appropriate patches, typically with
hg qpop -a hg qpush -a
To disregard all guarded patches one uses instead:
hg qselect -n sage -combinat qselect
Upgrading to the latest version of sage
With the sage-combinat script
See the simple instructions
By hand
When one runs "sage -upgrade", it will update the repository under $SAGE_ROOT/devel/sage-main and not touch the one under $SAGE_ROOT/deve/sage-combinat. Once an email goes out (to sage-combinat-devel) saying that the patch repository is ready to work with the new version of Sage, perform the following steps:
cd $SAGE_ROOT/devel/sage-combinat hg qpop -a #Remove all the old patches hg pull -u ../sage-main #Pull the new version of Sage from your local main repository cd .hg/patches hg pull -u #Pull the new versions of the patches cd ../../ hg qpush -a #Push on the new patches sage -b #Build the new changes
Using the sage-combinat patches with an older version of sage
For the convenience of the user, it is possible to use the sage-combinat patches with an older version of sage. For this, one needs to specify that the sage-combinat patches that were integrated into the latest sage version (and therefore are not applied by default) need to be applied. The intent is only to temporarily support one or two older versions of sage (that is about one month old); there is no guarantee whatsoever.
Note: this is taken care of automatically when using the sage-combinat script for installing or upgrading
cd $SAGE_ROOT/devel/sage-combinat hg qpop -a #Remove all the old patches cd .hg/patches hg pull #Pull the new versions of the patches hg update cd ../../ hg qselect 3_0_2 #Tell Mercurial that you want the patches that were included in 3.0.2 hg qpush -a #Push on the new patches sage -b #Build the new changes
Use and Contribute to the sage-combinat tree : step by step
See also the step by step instructions to contribute to sage-combinat.
